You have likely heard the term blockchain mentioned alongside Bitcoin or other digital currencies. But what is it, really? This guide demystifies the concept, breaking down what is blockchain technology into simple, understandable parts. We will explore how it works, why it is considered so secure, and how its applications are set to revolutionize industries far beyond finance, providing a clear path to understanding its true potential.
Understanding the basics of a block and a chain
At its core, what is blockchain technology? Imagine a shared digital record book. This book is a form of distributed ledger technology, composed of individual pages called blocks. Each block permanently records a list of transactions. Once a block is filled with data, it is added to the end of the book, creating a chronological chain of blocks. This simple but powerful structure is the foundation of its security and transparency.
Every block contains three essential elements that work together to maintain the integrity of the chain. These components are critical for the network to function correctly and securely.
- Data: This is the specific information recorded in the block. For a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, this data would include details of transactions.
- Hash: A unique cryptographic code, like a digital fingerprint. It identifies the block and all of its contents. Any change to the data inside creates a new hash.
- Hash of the previous block: This piece of data links one block to the next, creating a secure and unbreakable chain.
This interlocking system ensures that once a block is added, it cannot be altered. Changing a previous block would change its hash, breaking the entire chain that follows. This makes any attempt at tampering immediately obvious to everyone on the network.
How blockchain ensures security and transparency
The true innovation of what is blockchain technology lies not in storing data, but in the core features of its architecture. These characteristics work in concert to build a system that is inherently secure, transparent, and resistant to control by any single entity. This structure provides a foundation of trust without needing a central intermediary, which is one of the key benefits of blockchain.
Decentralization builds trust
Unlike a traditional database managed by one authority, a blockchain is decentralized. The ledger is copied and distributed across a network of computers. This means no single person or group holds control. For a new block to be added, the network must agree on its validity through a undefined. This process prevents unauthorized changes and eliminates a single point of failure.
Immutability creates a permanent record
Immutability means that once data is recorded, it cannot be changed. In a blockchain, transactions are locked into blocks with cryptography. Each block is securely linked to the one before it. Altering a past block would require immense computing power to change every subsequent block, making the data effectively tamper-proof. This creates a permanent and reliable audit trail.
Transparency provides clear visibility
On public blockchains like Bitcoin, transparency is a fundamental feature. While users’ real-world identities are kept private, all transaction records are public. Anyone can view the ledger to verify and trace transactions. This open access promotes accountability and builds trust among participants, as all actions are visible to the entire network.
Exploring the different types of blockchain networks

While core principles are shared, what is blockchain technology is not a single solution. Different types of networks exist, tailored for specific needs based on participation and data access. Understanding these public, private, and consortium models is key to grasping their diverse applications and how they work.
Public blockchains
Public blockchains are completely open and permissionless. Anyone can join the network, view the entire ledger, and participate in validating transactions. They are fully decentralized, offering the highest level of security against tampering. Bitcoin and Ethereum are the most famous examples of these open networks.
Private blockchains
A private or permissioned blockchain is controlled by a single organization. This entity restricts access and sets the rules for who can participate. This model offers effective undefined aiming to improve internal processes like supply chain management with greater security and efficiency.
Consortium blockchains
A consortium blockchain is a hybrid model governed by a select group of organizations. It blends the shared security of a public chain with the access control of a private one. This type is ideal for industry collaboration, such as multiple banks using a shared ledger to settle payments faster.
Beyond cryptocurrency what are the uses of blockchain
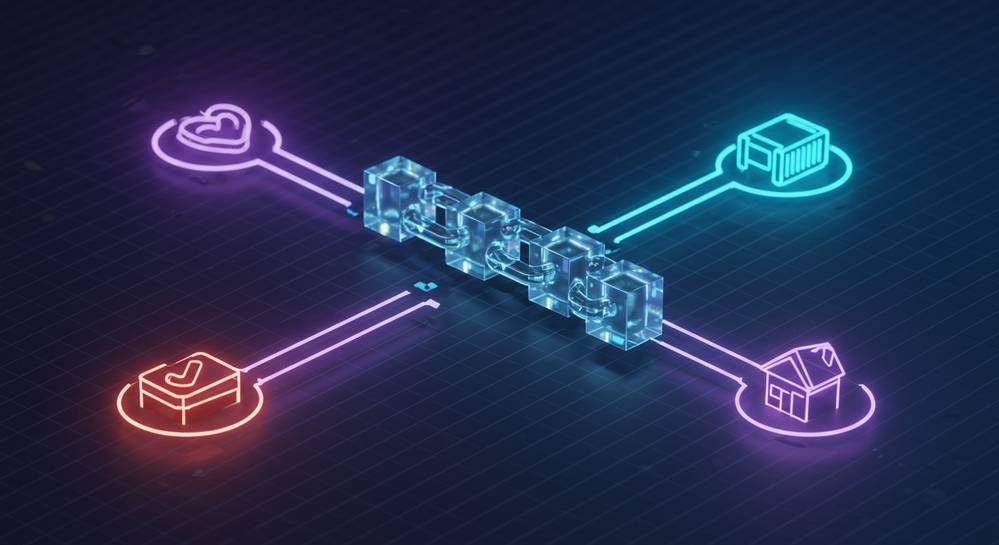
Although what is blockchain technology gained fame through cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its potential extends far beyond digital money. The ability to create a trusted, shared, and unchangeable ledger is revolutionizing numerous industries. This technology offers new ways to ensure trust and transparency in everyday processes.
- Supply Chain Management: Companies use blockchain to track products from origin to consumer. This creates a transparent, tamper-proof record that verifies authenticity, prevents counterfeits, and improves logistics efficiency.
- Healthcare: Blockchain can secure and unify patient medical records. It allows providers to access a patient’s history with permission, leading to better care while protecting privacy.
- Voting Systems: A blockchain-based voting system offers a way to cast votes that are both verifiable and anonymous. The immutable ledger ensures that once a vote is cast, it cannot be altered, increasing trust in election results.
- Intellectual Property: Artists and creators can use blockchain to establish a permanent, public record of ownership for their work. This helps manage copyrights and combat plagiarism effectively.
Blockchain technology is more than just a complex system for digital currencies; it is a foundational tool for building a new generation of trusted and transparent digital applications. It offers a robust framework for recording data securely and verifiably without relying on a central authority. To explore how these innovations are shaping our world, continue your journey at Solution Of Blockchain and discover the future of technology.
