What is near protocol sharding?
Is your blockchain struggling to keep up? NEAR Protocol sharding technology is the answer to unlocking unmatched scalability, lightning-fast transactions, and minimal fees.
What is near protocol sharding?
What is the NEAR Protocol?
Imagine a digital city where transactions and applications run smoothly, quickly, and without costing an arm and a leg. That’s what the NEAR Protocol aims to be: a foundation for building and using apps in a way that’s accessible to everyone, not just the tech-savvy.
The Magic of Sharding
Sharding is like dividing a big, bustling city into smaller, manageable neighborhoods. Each neighborhood can handle its own traffic, reducing congestion and allowing more people to go about their business quickly. In blockchain terms, this means more transactions can happen simultaneously, making the whole system faster and more efficient.
Near protocol sharding
NEAR Protocol’s sharding is a unique and innovative approach to blockchain scalability. It involves dividing the network into multiple parallel “shards,” each acting like a mini-blockchain capable of processing transactions and smart contracts independently. This parallel processing significantly enhances the network’s capacity and speed, allowing it to handle a much higher volume of transactions than traditional blockchains.
Key aspects of NEAR Protocol’s sharding
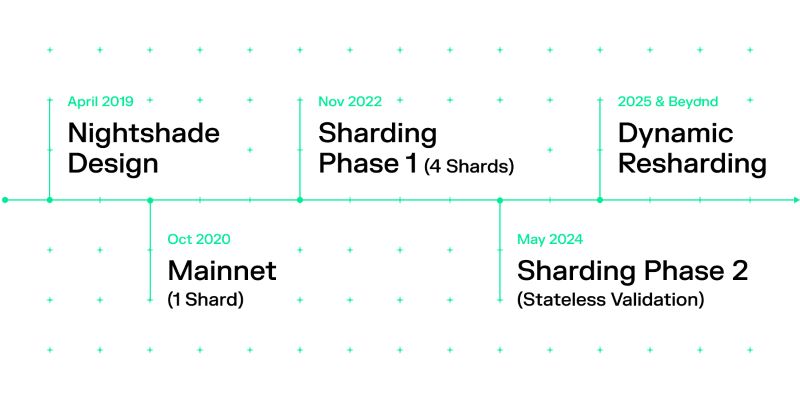
NEAR Protocol’s sharding is characterized by its Nightshade design, which divides the blockchain into multiple shards and employs a “chunk-only producer” approach to minimize the computational burden on individual nodes. Stateless validation allows validators to participate without storing the entire blockchain state, enhancing decentralization and scalability.
Dynamic resharding automatically adjusts the number of shards based on network demand for optimal performance. Additionally, NEAR’s sharding allows for composability, enabling cross-shard communication and the development of complex applications.
Benefits of NEAR Protocol’s Sharding
High Throughput: By dividing the network into shards, NEAR Protocol can handle an immense volume of transactions, potentially reaching millions per second. This scalability is crucial for widespread adoption and enables the network to support a growing ecosystem of decentralized applications.
Low Fees: The efficient design of NEAR’s sharding significantly reduces transaction costs, making it one of the most affordable platforms in the Web3 landscape. This affordability enhances accessibility for users and encourages greater adoption of decentralized applications.
Fast Finality: Transactions on NEAR Protocol are confirmed and finalized quickly, typically within a few seconds. This rapid finality ensures a smooth user experience and enables real-time applications to thrive on the network.
Decentralization: NEAR’s sharding model, combined with stateless validation and dynamic resharding, promotes a decentralized network where no single entity holds control over the entire blockchain. This decentralization enhances security and resilience, protecting the network from potential attacks and disruptions.
Drawbacks of NEAR Protocol’s Sharding
Complexity: Sharding is a technically complex solution. Implementing and maintaining a sharded blockchain requires expertise and resources, potentially increasing development costs and introducing vulnerabilities if not executed properly.
Security Concerns: While sharding aims to improve security by distributing the network, it can also introduce new attack vectors. For example, a single shard could become a target for malicious actors, and cross-shard communication can be vulnerable to exploits.
Data Availability Issues: Ensuring data availability across multiple shards can be challenging. If a shard fails or experiences a network outage, accessing the data stored on that shard could be difficult, potentially disrupting applications and services.
Centralization Risks: While NEAR’s sharding aims for decentralization, there are concerns about the potential for centralization in certain aspects, such as the governance process, where only validators currently have voting power.
Interoperability Challenges: While sharding allows for communication between shards, it can still pose challenges for interoperability with other blockchain networks that do not utilize sharding.
New and Unproven Technology: NEAR Protocol’s sharding is a relatively new technology, and its long-term viability and security are still being tested. While early results are promising, there is still a need for further research and development to address potential issues and ensure the system’s robustness.
The Leap to Phase 2
Phase 2 of NEAR Protocol’s sharding represents a significant leap forward, akin to upgrading individual neighborhoods with high-speed transportation and advanced communication tools. This phase introduces “stateless validation,” eliminating the need for each shard to maintain a full record of every transaction and piece of data.
Instead, shards can access this information from a central repository, similar to a city library, simplifying and accelerating the validation process. This upgrade promises to make NEAR Protocol even more efficient and scalable, unlocking its full potential as a leading blockchain platform.
Explore the innovative solutions offered by Solution of Blockchain and discover how NEAR Protocol’s sharding technology can transform your decentralized projects.