What are cryptocurrency layer 2 scaling technologies?
Is Ethereum’s slow transaction speed and high fees holding you back? Discover the layer 2 scaling technologies solutions that are revolutionizing the blockchain experience, making transactions faster, cheaper, and more efficient.
Why are scaling solutions necessary?
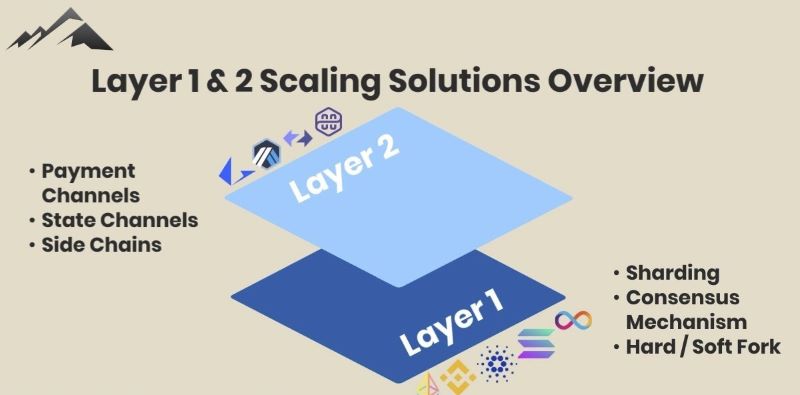
Layer 1 blockchain Technologies solutions enhance the scalability of the underlying protocol by modifying its fundamental operation. For instance, Ethereum’s transition from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus aims to achieve faster transactions and more energy-efficient mining.
Another Layer 1 scaling approach is sharding, which involves partitioning the blockchain into smaller segments to distribute the workload of validating and authenticating transactions across more nodes in the peer-to-peer network. This allows for quicker block completion and improved throughput.
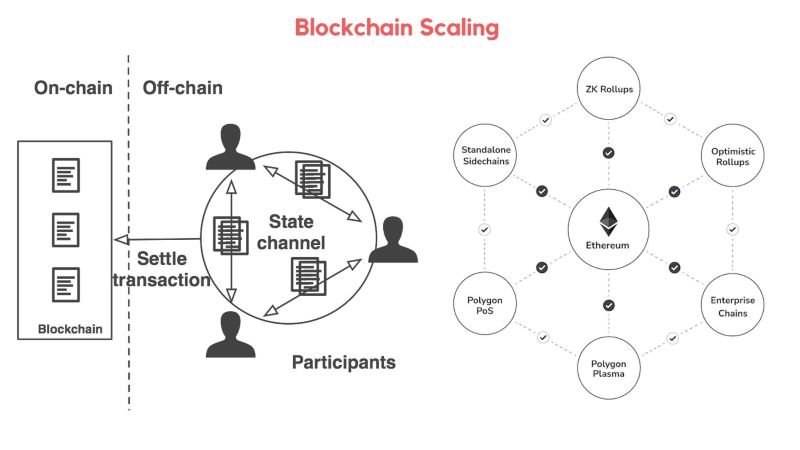
However, Layer 1 solutions are not the sole avenue for blockchain scalability. Layer 2 solutions introduce additional protocols built on top of existing blockchains like Ethereum or Bitcoin. These solutions enhance throughput while preserving the core decentralization and security principles of the underlying blockchain.
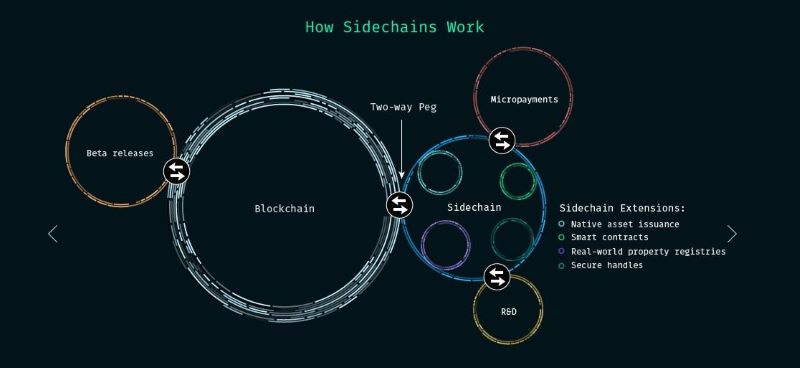
What Is a Sidechain?
Sidechains are a hybrid scaling solution, merging aspects of both layer 1 and layer 2 approaches. Essentially, a sidechain is a separate blockchain linked to a main chain like Bitcoin through a two-way peg (2WP), enabling the transfer of cryptocurrency between the two. However, this transfer requires a degree of trust in a third-party.
The Liquid Network, linked to Bitcoin’s main chain, is a prime example of a sidechain. Similar to other layer 2 solutions, it aims to address scalability challenges by offloading transaction validation and processing to a separate blockchain. This allows the main chain to handle a larger volume of transactions, thereby increasing its overall capacity and efficiency.
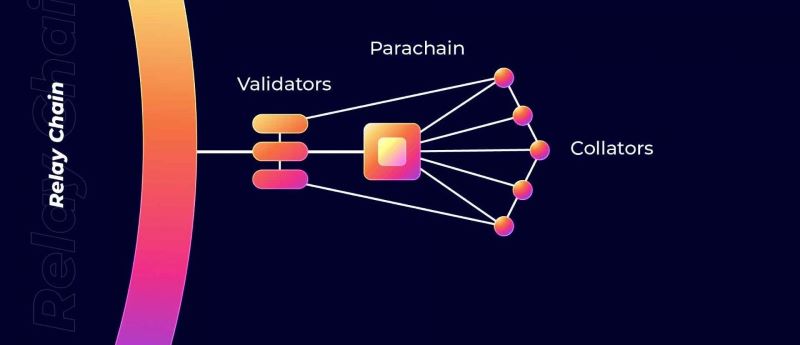
What Is a Parachain?
Parachains, or “parallel chains,” operate as interconnected blockchains within a larger network. They are built on a shared framework, ensuring uniform security attributes, and connect to a central relay chain. This allows them to function independently while still benefiting from the security and interoperability of the entire network.
The parallel nature of parachains enables efficient workload distribution, resulting in significantly faster transaction speeds. This concept is fundamental to Polkadot’s innovative approach to blockchain scalability and interoperability.
What Is Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum 2.0 is a major upgrade of the Ethereum network, transitioning it to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) system that incorporates sharding and other enhancements to address scalability issues. This upgrade aims to significantly boost transaction throughput, aligning Ethereum’s performance with leading blockchains. Moreover, it introduces staking opportunities for Ethereum investors, allowing them to earn rewards for their contributions to the network’s validation process.
What Is a Hashgraph?
Hashgraphs are a distributed ledger technology (DLT) distinct from blockchains. Unlike blockchains, hashgraphs are patented, with Hedera Hashgraph being the sole ledger utilizing this technology. Hedera Hashgraph positions itself as the third generation of public ledger technology, following Bitcoin and Ethereum. It boasts impressive scalability of 10,000 transactions per second (TPS), along with lower fees, reduced energy consumption, and faster processing times.
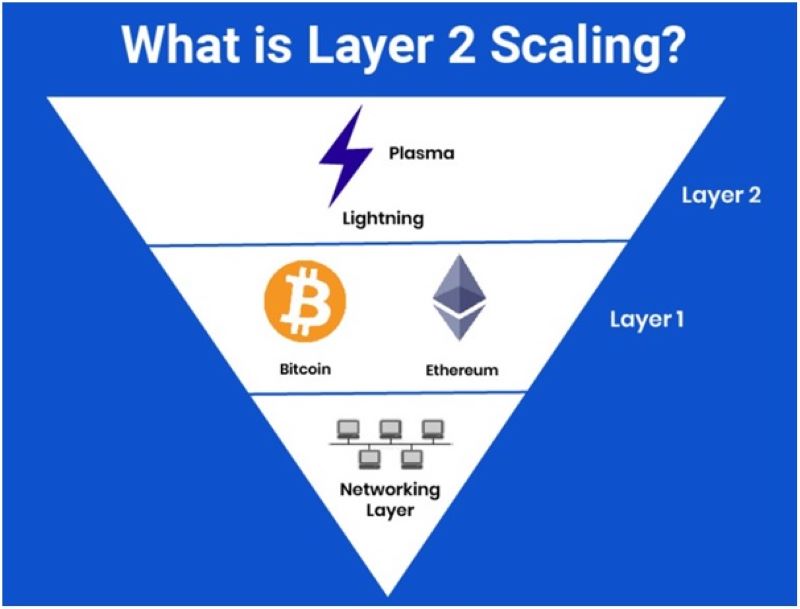
Types of Layer 2 Scaling technologies
Layer 2 scaling solutions are designed to enhance blockchain performance by inheriting security from the main chain, unlike sidechains which might rely on alternative networks or validators. Two prominent types of Layer 2 solutions are zero-knowledge rollups and optimistic rollups.
Layer 2 scaling engines like Starkware, Optimism, and Arbitrum are instrumental in providing scalability for blockchains like Ethereum, enabling a growing number of exchanges and platforms to utilize the network effectively.
Zero-Knowledge Rollups
Zero-knowledge rollups (ZK-Rollups) are bundles of data secured by a smart contract on the main blockchain, while the processing and computation occur off-chain. This approach enables faster block creation (around one minute) and higher transaction processing speed (2,000 TPS). The term “zero-knowledge” signifies that all verifiers can confirm they possess the same information without it being explicitly revealed.
ZK-Rollups outperform Layer 1 solutions due to off-chain data storage. Essential data for smart contracts is accessed less frequently, conserving processing power and freeing up blockchain capacity for transaction validation. Consequently, gas fees decrease, leading to faster and more cost-effective transactions.
Optimistic Rollups
Optimistic rollups operate directly on Ethereum’s base layer, enabling a large number of smart contracts to execute without overloading the network. They inherit the same security level as the main Ethereum chain, while data aggregators utilize merkle roots for faster transaction speeds. However, their throughput is not as high as Plasma or ZK-Rollups.
The key difference compared to ZK-rollups is the longer confirmation time for layer 2 transactions. Optimistic rollups require external validators to verify merkle roots before the state can be updated. On the other hand, optimistic rollups offer greater flexibility by supporting smart contracts in a way similar to the underlying blockchain.
Plasma
Ethereum’s Plasma is a layer 2 scaling solution that utilizes child or secondary blockchains to alleviate the main chain’s workload. These Plasma chains, akin to smart contracts or Polkadot’s parachains, are organized hierarchically to offload transactions from the main chain, enhancing scalability. This approach allows Ethereum to handle a larger volume of transactions by distributing the processing burden across multiple chains, ultimately improving the network’s overall efficiency and capacity.
Bitcoin Layer 2 Scaling Technologies Solutions
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is a prominent example of a Layer 2 solution designed to address Bitcoin’s scalability challenges. It operates by moving transaction bundles off the main blockchain for processing, then transferring the results back. This approach not only significantly increases transaction speed but also introduces the capability for smart contracts on Bitcoin.
The Lightning Network boasts several key advantages. It promises near-instantaneous transactions, potentially reaching speeds of milliseconds, a vast improvement over Bitcoin’s typical 10-minute average. Additionally, it claims to handle a massive volume of transactions per second, far surpassing traditional payment systems. By settling transactions off-chain, it drastically reduces fees, enabling micropayments. Furthermore, it facilitates cross-chain atomic swaps between blockchains sharing the same cryptographic hash function.
More detailed information about the Bitcoin Lightning Network can be found through relevant resources.
Ethereum Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
Starkware
StarkWare, a leader in Ethereum layer 2 scaling solutions, offers three key products: StarkNet, StarkEx, and Cairo.
StarkNet is a permissionless decentralized ZK-rollup designed for the Ethereum blockchain. Developers can deploy their smart contracts without restrictions on StarkNet’s testnet, benefiting from unlimited scalability while retaining Ethereum’s composability and security.
StarkEx is a proven layer 2 scalability engine deployed on the mainnet since June 2020. It caters to various use cases and serves notable clients like DeversiFi, Immutable, and dYdX. StarkEx’s strengths lie in its trustless scalability through ZK-STARK technology, enabling the creation of self-custodial dApps and providing a robust scaling solution for diverse applications.
Cairo, StarkWare’s Turing-complete language, underpins both StarkNet and StarkEx. It allows for the scaling of dApps using STARKs, ensuring efficient and secure operations.
Optimism
Optimism, a Layer 2 scaling solution compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), offers a fast, simple, and secure platform for decentralized applications. Users can seamlessly transfer assets in and out of the network through the Optimistic Ethereum Gateway. Projects seeking deployment can apply for whitelisting, with a streamlined approval process for those meeting the launch criteria. This accessibility and ease of use led to the successful alpha launch of Uniswap V3 on Optimism’s mainnet in July 2021.
Arbitrum
Arbitrum is a Layer 2 scaling solution designed to enhance the speed and scalability of Ethereum smart contracts, while simultaneously offering improved privacy features. It enables developers to run existing Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) contracts and transactions on its Layer 2 network, without compromising the security of the underlying Layer 1 blockchain (Ethereum).
Specifically tailored for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, Arbitrum leverages its rollup technology to scale any Ethereum contract, making it a valuable tool for projects seeking to overcome Ethereum’s limitations.
Developed by Offchain Labs, Arbitrum launched its Ethereum mainnet beta, Arbitrum One, in August 2021, securing substantial funding and demonstrating its commitment to revolutionizing the Ethereum ecosystem.
Polygon
Polygon is another layer-two solution for Ethereum, leveraging different technologies to enhance Ethereum’s scalability:
- Polygon PoS: EVM-compatible sidechain.
- Polygon Miden: a zk-rollup based on Starkware.
- Polygon Hermez: an open-source zero-knowledge rollup.
- Polygon Avail: a standalone layer-2 chain with a data availability focus.
- Polygon Zero: a zk-rollup chain.
- Polygon Nightfall: a privacy-focused rollup chain.
Learn more in our deep dive into Solution of Blockchain.