How to use smart contracts for business: A step-by-step guide
How to use smart contracts for business: Unlock the power of smart contracts for business efficiency and security. Discover how to streamline transactions and automate processes using smart contracts, revolutionizing the way you conduct business.
How to use smart contracts for business?
A smart contract—like any contract—is an agreement between two parties. Smart contracts use code to leverage the benefits of blockchain technology, including efficiency, transparency, and security. The results can be innovative, but using smart contracts also carries risk.
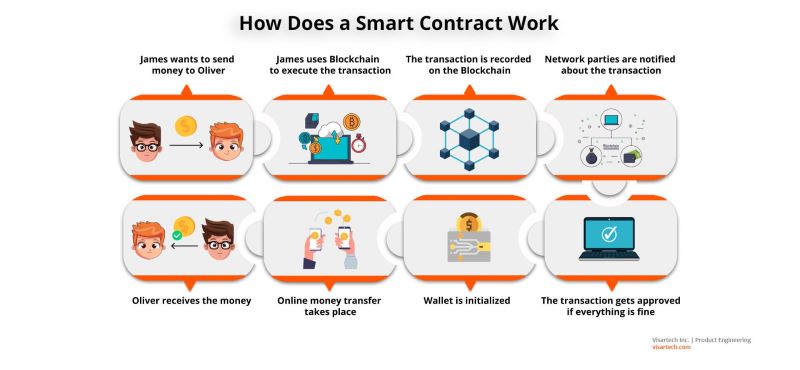
The digital nature of smart contracts means they can be programmed to execute automatically in a six-step process.
Agreement on Terms
Parties agree on the terms and conditions of the transaction, including how the smart contract will operate and under what conditions it will execute.
Smart Contract Creation
The agreed-upon terms are translated into code to create the smart contract, ensuring it specifies rules and consequences similar to a traditional legal contract. It’s crucial to ensure the smart contract’s security during this stage.
Deployment to Blockchain
Once the smart contract is securely designed, it is deployed to a blockchain through a transaction, making it live and immutable.
Triggering Conditions
The smart contract monitors the blockchain for specific conditions or triggers, such as reaching a certain date or completing a payment.
Execution
When trigger conditions are met, the smart contract executes predefined actions automatically, such as transferring funds or registering ownership of an asset.
Recording to Blockchain
The execution of the smart contract is recorded on the blockchain as a transaction, providing a transparent and immutable record of the contract’s outcome.
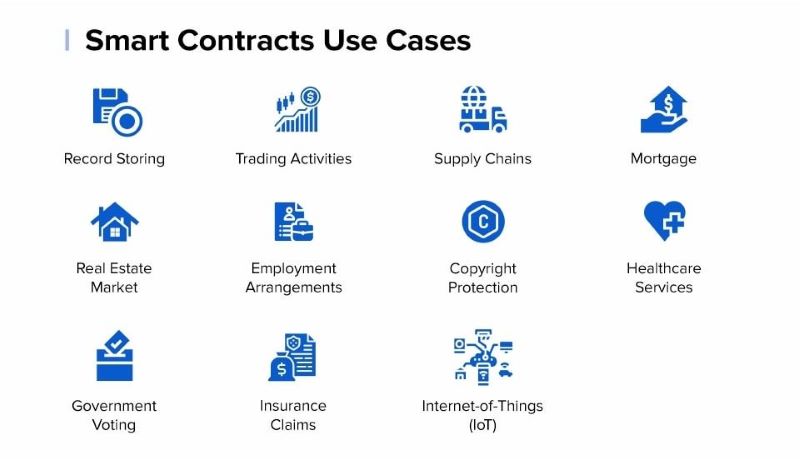
Use cases for smart contracts
Smart contracts offer a myriad of use cases across various domains, revolutionizing traditional processes and enhancing efficiency. Here are some specific examples:
Automatic Savings: Utilize smart contracts to automate monthly savings by transferring funds to a designated account, promoting disciplined saving habits.
Automatic Investing: Implement smart contracts to automate investment activities, streamlining buy and sell decisions while reducing direct involvement.
Insurance Claims: Accelerate the insurance claims process by leveraging smart contracts to automate claim submissions and payouts based on verifiable events, such as natural disasters.
Estate Planning: Integrate smart contracts into estate plans to automate the distribution of digital assets upon the individual’s demise, potentially bypassing lengthy probate procedures.
Peer-to-Peer Lending: Facilitate peer-to-peer lending through smart contracts, enabling transparent and secure lending transactions without the need for intermediaries.
These examples merely scratch the surface of the extensive range of potential smart contract applications. From decentralized finance to supply chain management, smart contracts hold the promise of transforming numerous aspects of our daily lives and business operations.
Are smart contracts secure?
Smart contracts operate by monitoring the blockchain or other credible sources for specific conditions or triggers. These triggers encompass various digitally verifiable events, such as reaching a date, completing a payment, or receiving a monthly bill. Once trigger conditions are met, the smart contract executes, performing actions like transferring funds or registering ownership. The contract’s execution is recorded on the blockchain for transparency.
As for smart contract security, developers can enhance it by prioritizing secure coding practices, rigorous testing, regular audits, and performance verification. However, smart contracts may still face risks such as legal enforceability, interoperability issues, coding errors, network congestion, and transaction fees. Evaluating and ensuring the security of smart contracts is crucial, involving a combination of technical measures, legal considerations, and continuous monitoring and upgrading.
In summary, smart contracts represent a groundbreaking technology that automates agreements based on predefined rules. Their ability to execute transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks or attorneys holds immense promise. By leveraging blockchain technology, smart contracts create tamper-proof and automated systems, reducing reliance on centralized institutions and fostering trust in code.
However, relying solely on computer code for critical tasks carries inherent risks. Many remain hesitant to use smart contracts for significant transactions, given the lack of reversibility and evolving legal frameworks. Despite these challenges, the growing adoption of smart contracts hints at their potential to reshape our economy and society in the future, albeit with careful consideration of their implications.
To explore the potential of smart contracts further and stay informed about their evolving role in our economy and society, consider staying updated on blockchain technology and its applications. Contact Solution of Blockchain today to learn more and fortify your blockchain solutions.