Unlock a Multiverse of Possibilities: Discovering Ethereum Virtual Machine Compatibility and its Impact on the Blockchain Landscape
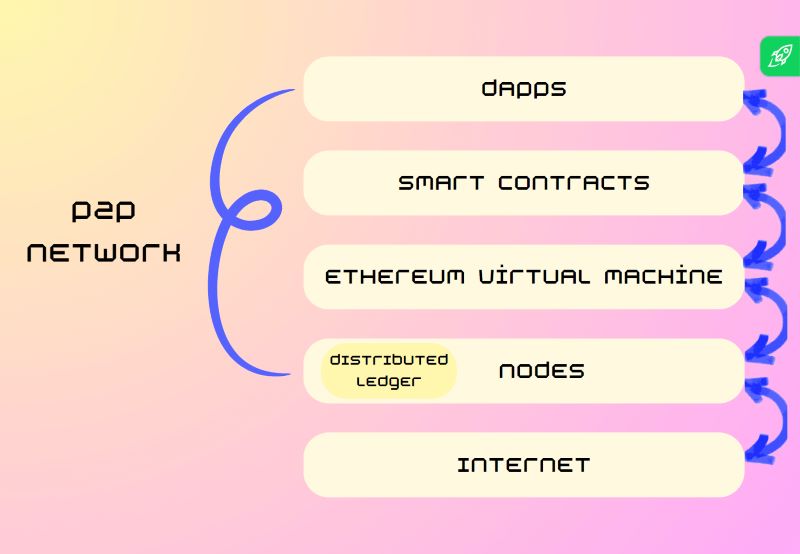
What is Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)?
Essentially, the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a virtual machine, or a cloud computer, functioning as a decentralized runtime environment for smart contract execution. These self-executing contracts enable trustless and immutable transactions, paving the way for a transformative change in decentralized application (DApp) development.
Moreover, several blockchains, including BNB Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, and Fantom, are compatible with the EVM. This compatibility means they adhere to the same standards and protocols as the Ethereum network, fostering a cohesive and interoperable ecosystem for decentralized applications.
The Technical Makeup of Ethereum Virtual Machine
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) boasts a robust technical makeup, comprised of essential elements like the stack, memory, storage, and execution environment. The stack plays a crucial role in managing data during the execution of smart contracts, while memory temporarily holds variables used in computations. Storage, on the other hand, serves as a persistent repository for contract data, ensuring its availability across transactions.
The execution environment, encompassing the consensus mechanism, guarantees the seamless and secure processing of transactions. This environment ensures that all nodes in the network agree on the state of the blockchain and the outcome of smart contract executions, maintaining the integrity and reliability of the Ethereum network.
Ethereum Virtual Machine compatibility
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatibility refers to the capability of a blockchain network to understand and execute smart contracts written in the Ethereum programming language, Solidity. This means developers can easily port their existing Ethereum-based dApps (decentralized applications) onto these compatible blockchains without requiring substantial code modifications.
The key advantage of EVM compatibility is its ability to foster interoperability between different blockchain networks. This allows for the seamless transfer of assets and data, as well as the ability to leverage the existing Ethereum developer community and tools.
EVM compatibility has become a significant factor in the blockchain landscape, with numerous networks adopting this standard to attract developers and users from the Ethereum ecosystem. This has led to the growth of a multi-chain ecosystem where EVM-compatible blockchains can coexist and collaborate, offering greater flexibility and scalability for decentralized applications.
How EVM Works with Smart Contracts and DApp
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the driving force behind the execution of smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. These smart contracts, coded in languages such as Solidity, are self-executing agreements that automate processes and transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries. By leveraging the decentralized nature of the EVM, decentralized applications (DApps) ensure enhanced security and transparency for users.
Benefits and Limitations of Ethereum Virtual Machine
Benefits
Smart Contract Execution: EVM’s primary strength lies in its ability to execute smart contracts, enabling the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) with automated, trustless, and transparent functionalities.
Decentralization and Security: EVM operates on a decentralized network of nodes, ensuring that no single entity controls the execution of smart contracts. This decentralization, combined with cryptographic security, makes it highly secure and resistant to tampering.
Immutability: Once a smart contract is deployed on the EVM, its code becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or reversed. This ensures the integrity of the contract and protects against unauthorized modifications.
Turing Completeness: EVM is Turing complete, meaning it can theoretically compute anything that a regular computer can, allowing for a wide range of complex and customizable smart contracts.
Interoperability: EVM compatibility is becoming increasingly popular, enabling the seamless migration of dApps between different blockchain networks and fostering a more interconnected ecosystem.
Limitations
Scalability: One of the major challenges facing EVM is scalability. As the number of transactions and dApps on the Ethereum network grows, the EVM can become congested, leading to slower transaction speeds and higher gas fees.
Cost: Executing smart contracts on the EVM requires computational resources, which are paid for in the form of gas fees. These fees can become expensive, especially during periods of high network congestion, limiting the accessibility of dApps for some users.
Complexity: Developing and deploying smart contracts on the EVM requires specialized knowledge and expertise, creating a barrier to entry for some developers.
Security Vulnerabilities: While the EVM is generally secure, smart contracts themselves can have vulnerabilities that can be exploited by hackers. This highlights the importance of thorough code audits and best practices in smart contract development.
Limited Upgradability: Once a smart contract is deployed on the EVM, it cannot be easily modified or updated, making it challenging to fix bugs or implement improvements. This can lead to potential issues with the functionality and security of dApps over time.
Understanding EVM’s Interaction with the Ethereum Network
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is deeply integrated with the Ethereum network, serving as its operational engine. It processes and executes smart contracts, ensuring consistent outcomes across all nodes. Gas fees, paid in Ether (ETH), are used to allocate resources and incentivize node operators for their computational contributions. This interaction between the EVM and the Ethereum network maintains the decentralized and trustless nature of the blockchain, while also powering the diverse range of applications and services built on top of it.
The Future of Ethereum Virtual Machines
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) stands as the cornerstone of the Ethereum blockchain’s success, empowering decentralized application (dApp) development and smart contract execution. However, the EVM’s future holds even more exciting possibilities.
With the transition to Ethereum 2.0, the EVM will undergo significant upgrades to enhance scalability and efficiency. The introduction of sharding, a technique that divides the network into smaller segments for parallel processing, will alleviate congestion and increase transaction throughput. Additionally, the switch from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake consensus will further improve efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Furthermore, ongoing research and development are focused on optimizing the EVM for specific use cases, such as privacy-focused applications and high-performance computing. This specialization will lead to the creation of more tailored and efficient virtual machines, catering to the diverse needs of the blockchain ecosystem.
As the EVM evolves, it will continue to play a central role in maintaining the integrity of decentralized applications and providing a standardized environment for developers. This will ensure that Ethereum remains a leading platform for innovation and growth in the decentralized world.
The future of the EVM is bright, with ongoing improvements and a large developer community driving its evolution. As new challenges arise and technologies emerge, the EVM will adapt and innovate to meet the demands of the ever-changing blockchain landscape. The possibilities are endless, and the EVM is poised to remain a key player in the future of decentralized technology.
EVM’s Impact on Blockchain Development and Adoption
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) has had a profound impact on blockchain development and adoption. Developers can leverage EVM’s capabilities by optimizing smart contracts for gas efficiency, utilizing layer 2 scaling solutions, and actively engaging with the Ethereum community. This strategic approach maximizes the benefits of EVM and ensures seamless integration into various blockchain projects.
EVM’s user-friendly environment and robust features have been instrumental in driving the adoption of blockchain technology. As the primary engine for decentralized applications, EVM has played a pivotal role in fostering the growth of numerous popular crypto ecosystems. Its accessibility and versatility have empowered developers to create innovative solutions across various industries, further solidifying its position as a cornerstone of the decentralized web.
Key Takeaways on Ethereum Virtual Machines
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the cornerstone of the Ethereum blockchain, providing a secure and efficient platform for the execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications. By fostering trustless transactions and enhancing transparency, it has become an indispensable component of the blockchain ecosystem.
As we venture further into the ever-evolving world of blockchain technology, the EVM remains a steadfast driver of innovation and a key player in shaping the decentralized future. Its importance transcends its technical capabilities, embodying the core principles of trust, transparency, and collaboration that underpin the blockchain ethos.
Eager to explore the transformative potential of Ethereum Virtual Machines (EVMs) for your blockchain projects? Look no further! Our team of experts at Solution of Blockchain is ready to guide you through the intricacies of EVM development, offering tailored solutions and cutting-edge strategies to unleash the full power of decentralized applications. Contact us today to embark on your journey towards a decentralized future.