Tired of intermediaries, data breaches, and slow transactions? Discover the revolutionary potential of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), the foundation of blockchain and a game-changer for transparency, security, and efficiency in the digital age.
What is distributed ledger technology (DLT)?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) refers to the technological framework and protocols that enable simultaneous access, validation, and record updates within a networked database. It serves as the foundation for creating blockchains, providing a transparent and secure way to track and verify transactions or any digital interactions.
With DLT, every change to the database is visible to all authorized users, fostering transparency and accountability. This eliminates the need for extensive data auditing, as the system inherently ensures data reliability and integrity. Moreover, DLT allows for granular control over data access, restricting it to only those who need it, enhancing privacy and security.
How do distributed ledgers work?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) refers to the technological framework and protocols that enable simultaneous access, validation, and record updates within a networked database. It serves as the foundation for creating blockchains, providing a transparent and secure way to track and verify transactions or any digital interactions.
With DLT, every change to the database is visible to all authorized users, fostering transparency and accountability. This eliminates the need for extensive data auditing, as the system inherently ensures data reliability and integrity. Moreover, DLT allows for granular control over data access, restricting it to only those who need it, enhancing privacy and security.
History of Distributed Ledgers
Distributed computing, the foundation of distributed ledgers, has a long history, dating back several decades. In the 1990s, it allowed multiple computers and users in different locations to collaborate on problem-solving, centralizing the solutions.
Advancements in data science, computing, and related technologies have significantly enhanced the capabilities of ledgers. Improved connectivity through intranet and internet protocols facilitated the collection, analysis, and utilization of vast amounts of data. However, with increased access came the necessity for change verification.
Computer and data scientists addressed this challenge by developing programs that reduced the need for manual data auditing. These programs employed automation and data encryption techniques to validate database transactions or changes. This concept of consensus, involving automated agreement on transaction validity among a majority, became a cornerstone of distributed ledger technology.
How Distributed Ledger Technology Works
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) ensures secure and accurate information storage through cryptography. Data access is controlled by keys and cryptographic signatures, creating an immutable database governed by pre-defined network rules.
Due to their decentralized nature, privacy, and encryption, DLTs are less susceptible to cyberattacks. Successful attacks would require simultaneously compromising all copies of the ledger across the network. Additionally, peer-to-peer sharing and updating of records streamline the process, making it faster, more efficient, and cost-effective.
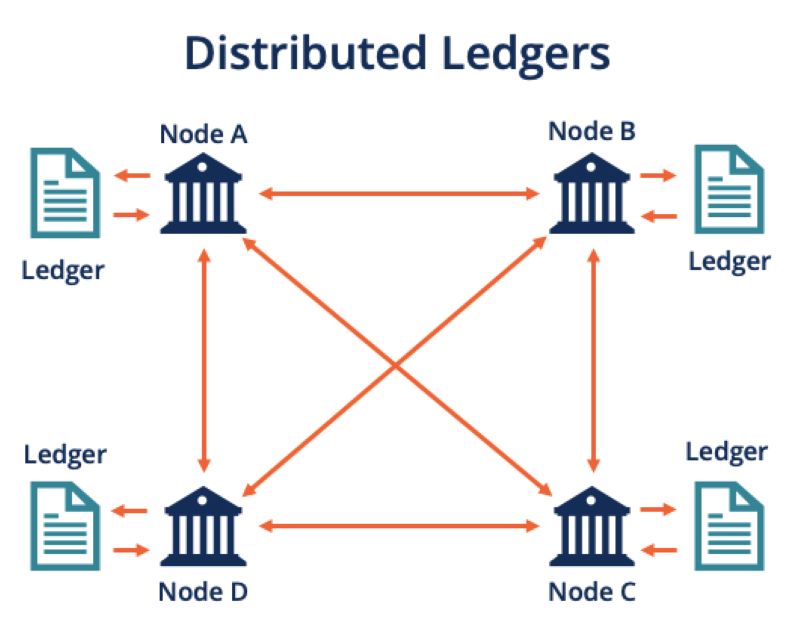
Each device, or node, in a DLT network holds a copy of the ledger, allowing them to record any changes. Nodes then publish their updated versions, including the latest transactions. If the network achieves consensus on the legitimacy of the latest ledger, these transactions are finalized, encrypted, and used as the basis for future transactions. This is how blockchains grow, with each block containing encrypted data linking it to the previous one, ensuring immutability.
Industries using Distributed Ledger Technology
Distributed ledgers are versatile and have found applications in various industries, including aviation, education, healthcare, insurance, manufacturing, transportation, and utilities. Notably, they are being utilized to transform supply chains, an area traditionally plagued by inefficiencies, inaccuracies, and vulnerabilities.
Fujitsu, a global tech leader, has developed a DLT solution to address these issues. Its Rice Exchange platform enhances supply chain transparency and prevents fraud by securely recording and tracking data throughout the rice trading process. From sourcing and pricing to insurance, shipping, and settlement, all relevant information is immutably recorded on the ledger, accessible to all involved parties.
This system not only ensures data accuracy and prevents tampering but also streamlines the entire process. With automated data entry and tracking, even the location of rice shipments can be monitored in real-time, ultimately enhancing efficiency and trust within the supply chain.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Distributed Ledger Technology
Advantages
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) offers numerous advantages over traditional systems, including enhanced resilience, security, transparency, and efficiency. It eliminates single points of failure, protects against data tampering, and fosters trust through transparent access to information. Additionally, DLT streamlines processes and promotes financial inclusion by removing intermediaries and leveraging smart contracts.
Disadvantages
However, DLT also faces challenges such as complexity in implementation and maintenance, potential scalability issues, and environmental concerns for energy-intensive systems. The lack of standardized regulations and potential privacy concerns further complicate its adoption. Despite these hurdles, DLT holds immense potential to revolutionize various industries if these challenges can be effectively addressed.
DLT is transforming industries by providing a decentralized, transparent, and secure way to record and verify transactions. As this technology continues to evolve, it holds the promise of revolutionizing how we manage data, conduct business, and interact with each other in the digital world.
Subscribe to the Blockchain Bulletin Weekly newsletter for expert insights, in-depth analysis, and exclusive content on the cutting edge of blockchain and distributed ledger technology.