What is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)? All about DPoS
Imagine a blockchain where you have a say in who validates transactions. That’s the idea behind Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), a consensus mechanism that introduces a democratic element to the blockchain world. Explore how DPoS combines efficiency, scalability, and community participation to power a new generation of decentralized networks.
What is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)?
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a consensus mechanism in blockchain technology that introduces a democratic element to the traditional Proof of Stake (PoS) system. In DPoS, users vote for delegates, who are responsible for validating transactions and creating new blocks. This approach addresses some of the limitations of PoS, offering a more affordable, efficient, and equitable way to secure the network and reach consensus.
The History of DPoS
The roots of Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism date back to 2012 when Peercoin became the first functional implementation. However, the concept of Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) was born in 2013, thanks to Daniel Larimer’s innovative vision. A year later, DPoS emerged as a refined version of the original PoS algorithm. In 2015, BitShares marked a significant milestone as the first iteration of DPoS, setting the stage for its continued evolution and adoption in the blockchain world.
How does Delegated Proof of Stake work?
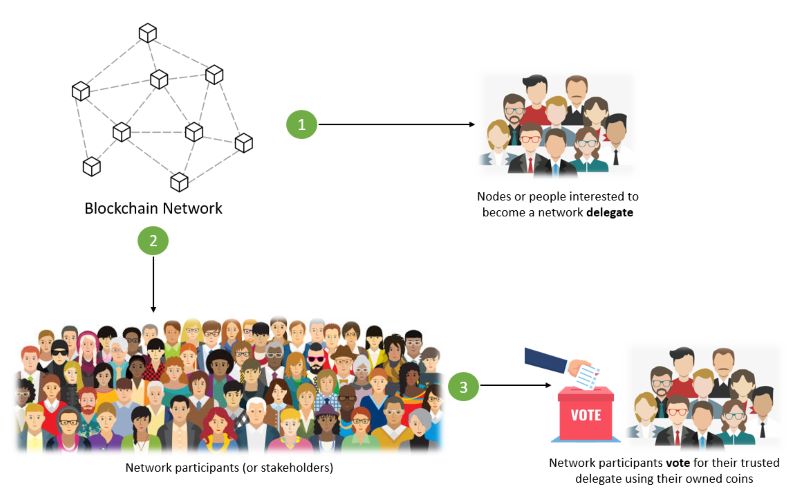
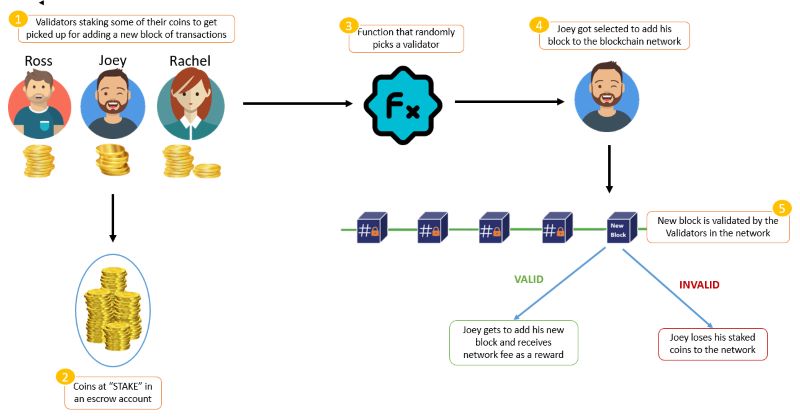
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) operates through a democratic process where network users vote to elect delegates, also known as witnesses or block producers, who are responsible for validating blocks and securing the network.
The number of delegates for each block is limited and varies depending on the blockchain. This ensures a dynamic system where delegates may change from block to block.
Users vote for delegates by pooling their tokens into staking pools and linking them to specific delegates. The delegate with the most votes earns the right to validate a block and receive transaction fees as a reward. These rewards are then distributed among the supporting users proportionate to their stake.
Crucially, users retain control over the system by having the power to vote out delegates if they engage in malicious activities. This accountability mechanism incentivizes delegates to maintain a good reputation and act in the best interest of the network.
Advantages of DPoS
Accessibility: The absence of specialized equipment requirements allows anyone to participate as a delegate, promoting inclusivity and democratizing the validation process.
Democracy: The low barrier to entry encourages broader participation in the consensus process, fostering a more democratic and financially inclusive ecosystem.
Scalability: The limited number of delegates enables faster consensus, resulting in improved network performance and higher transaction throughput.
Environmental Friendliness: DPoS requires significantly less energy compared to proof-of-work mechanisms, contributing to a more sustainable and eco-friendly blockchain network.
Disadvantages of DPoS
Centralization: Despite its intent to address centralization, DPoS can ironically lead to a concentration of power in the hands of a few delegates. This limited number of decision-makers raises concerns about potential collusion or manipulation of the network, including vote buying and the pushing of malicious transactions.
Malicious Delegates: The limited number of delegates also increases vulnerability to 51% attacks, where a majority of delegates act maliciously to control the network. Additionally, the ability for token holders to delegate their voting power opens the door for bribery and corruption, allowing malicious actors to gain control and manipulate the system.
Dependence on Delegators: DPoS relies heavily on active and informed delegators to maintain its integrity. This requires users to research delegates and actively participate in voting, which can be a barrier for those with smaller stakes who may feel their vote is insignificant.
DPoS Vs NPoS: What’s the Difference?
So now you know all about delegated proof of stake, you might have noticed its similarities to another consensus mechanism: Nominated proof of stake. Despite their similarities, these two methods differ slightly.
| Feature | Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) | Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS) |
| Validator Selection | Elected delegates validate blocks | Validators nominated and elected by stakeholders |
| Number of Validators | Limited, typically a few dozen | Larger pool of validators |
| Stakeholder Role | Vote for delegates | Nominate and elect validators |
| Accountability | Delegates can be voted out | Validators can be slashed for misbehavior |
| Efficiency | Generally faster transaction times | Can be slower than DPoS |
| Decentralization | Less decentralized due to fewer validators | More decentralized with a larger validator set |
| Examples | EOS, Tron, Steemit | Polkadot, Kusama |
Understanding Consensus Mechanisms: Does It Matter?
With the vast array of blockchain projects available, each with varying levels of centralization and different consensus mechanisms, it’s crucial to understand their implications. Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) offers benefits but raises concerns about true decentralization, a cornerstone of blockchain technology.
The essence of blockchain lies in decentralization, empowering users with control over their assets and data. This is why non-custodial wallets, like Ledger, are vital. These hardware wallets store private keys offline, ensuring that only you control your funds, shielding them from online threats.
Ledger not only empowers you to be your own bank but also enables interaction with decentralized applications (dApps) and Web3 platforms through secure integrations. Thus, it allows you to fully explore the crypto ecosystem with peace of mind.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) offers a unique blend of efficiency, scalability, and democratic governance. While not without its challenges, DPoS is a significant innovation in blockchain consensus mechanisms, providing an alternative to traditional Proof of Work and Proof of Stake systems. Understanding DPoS is key to grasping the evolving landscape of decentralized technologies.
Stay informed about the latest developments in DPoS and other blockchain consensus mechanisms. Follow Blockchain Bulletin Weekly newsletter for in-depth analysis, expert insights, and exclusive content on the cutting edge of blockchain technology.