Decentralized physical infrastructure network (DePIN)? All about you need to know
What if essential resources like internet and energy were controlled by the people, not corporations? Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks, or DePINs, are making this a reality.
What does DePIN mean?
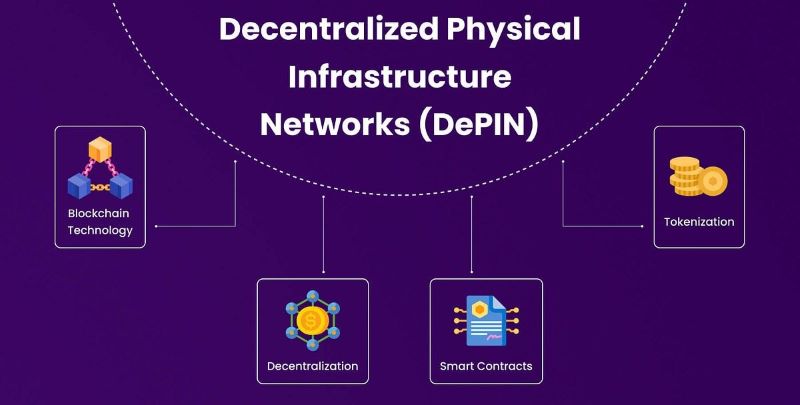
Decentralized physical infrastructure networks (DePIN) encompass the application of blockchain technology and decentralization principles to tangible infrastructure systems. The rise of blockchain has ushered in a paradigm shift in how we perceive digital systems, revolutionizing aspects like decentralized finance and nonfungible tokens. However, this revolution is not confined to the virtual realm.
DePINs extend the ethos of decentralization to physical infrastructure, potentially reshaping industries and empowering individuals in unprecedented ways. Through technologies like smart contracts and the Internet of Things (IoT), DePINs enable autonomous, real-time interactions within physical infrastructures, enhancing their responsiveness and adaptability to human needs.
Blockchain’s impact on the lives of ordinary citizens is evident through DePINs. By leveraging blockchain, DePINs enhance security, efficiency, and transparency in physical systems like renewable energy grids and supply chains. For example, they can provide immutable records of product provenance in supply chains, ensuring authenticity and traceability.
Furthermore, DePINs can enable peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading, democratizing access to energy resources by allowing households with solar panels to sell surplus energy to neighbors. Integrating renewable energy sources into DePINs not only ensures sustainable power for blockchain operations and IoT devices but also reduces their environmental impact.
Another vital component of DePINs is the integration of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), which facilitate self-governance and independent decision-making. This allows stakeholders to collectively guide the network’s development, fostering a more equitable and participatory ecosystem.
Origin and evolution of DePINs
The roots of DePINs can be traced back to the early exploration of blockchain’s potential beyond digital currencies. Projects like Power Ledger and OpenBazaar demonstrated the feasibility of decentralizing energy distribution and e-commerce, respectively. Power Ledger empowered individuals to trade excess energy directly, creating a more efficient and sustainable energy ecosystem. OpenBazaar enabled peer-to-peer transactions, eliminating intermediaries in online commerce.
As the concept gained momentum, new initiatives expanded the scope of DePINs. Helium utilized blockchain to build a decentralized wireless network, rewarding individuals for providing coverage. Render introduced a decentralized cloud computing platform, offering a scalable and cost-effective alternative to centralized services. Filecoin revolutionized decentralized storage by leveraging blockchain to establish secure, distributed networks where participants could monetize their unused storage space.
These early projects laid the groundwork for the burgeoning DePIN ecosystem, showcasing the transformative potential of blockchain technology in revolutionizing physical infrastructure and services.
How do Decentralized physical infrastructure networks work?
DePINs operate by distributing control and management of physical infrastructure across a network, utilizing blockchain technology to ensure transparency and trust. They encompass diverse domains, from energy systems and supply chains to telecommunications, data storage, transportation, and real estate.
To illustrate, consider a decentralized energy grid as a DePIN application. Here, individual homes with solar panels can generate and sell excess electricity directly to the grid or neighbors, bypassing centralized utilities. Every transaction, whether production, consumption, or sale, is recorded on the blockchain, fostering transparency and trust. Smart contracts automate these transactions based on predefined conditions, ensuring efficient energy distribution.
This decentralized model optimizes energy distribution based on real-time supply and demand, promoting renewable energy sources and reducing reliance on centralized power plants. It empowers individuals to become both producers and consumers of energy (“prosumers”), making energy access more democratic and equitable.
Some DePINs incentivize participation through cryptocurrency rewards for contributed energy. These tokens motivate stakeholders to invest in, maintain, and utilize the infrastructure, ensuring its growth and sustainability.
In the crypto world, DePINs can also take the form of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, utilizing blockchain for financial services without traditional intermediaries. They can even interact with real-world assets through tokenization, where tangible assets are represented as digital tokens on the blockchain for decentralized ownership and trading.
In essence, DePINs revolutionize how we approach infrastructure by decentralizing control, promoting transparency, and empowering individuals and communities to actively participate in and benefit from these networks.
Architectural considerations for scaling DePIN applications on blockchain infrastructure
To scale DePIN applications effectively on blockchain infrastructure, certain architectural considerations are paramount. The underlying blockchain must be capable of handling high transaction volumes and data throughput to meet the demands of decentralized physical networks.
Transaction economics are crucial, as the sheer number of transactions in DePIN applications necessitates low fees for sustainability. A blockchain struggling with high fees under increased transaction volume is unsuitable for DePIN projects.
Interoperability with other blockchains and legacy systems is essential for seamless communication and data exchange within DePIN applications.
Robust security measures, including encryption, authentication, and consensus algorithms, are non-negotiable to protect sensitive information and maintain the integrity of DePIN networks.
Lastly, user-friendliness is key to widespread adoption. Intuitive interfaces and straightforward designs enable individuals and organizations to participate in DePIN ecosystems without requiring extensive technical expertise.
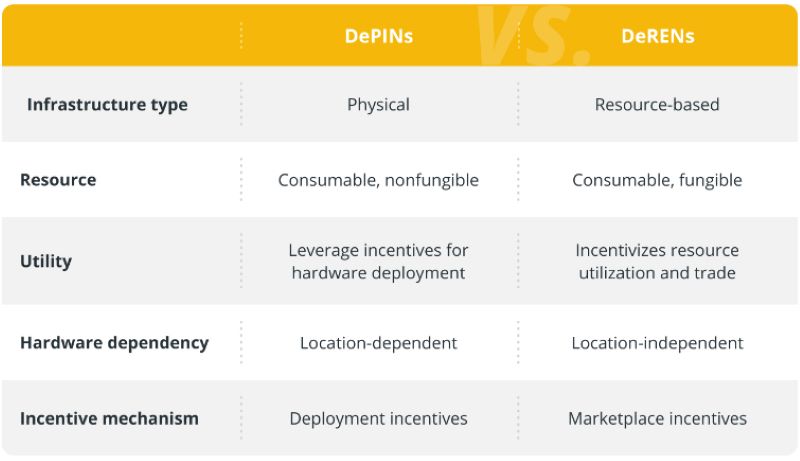
DePINs vs. DeRENs
While DePINs primarily focus on decentralizing physical infrastructure, DeRENs concentrate on virtual and resource-based aspects. These two paradigms within decentralized systems cater to different areas of development.
DePINs tackle the challenge of building decentralized networks for tangible infrastructure like communication, energy, and transportation. This approach aims to reduce reliance on centralized entities, improving accessibility, efficiency, and resilience by distributing control and resources across multiple nodes.
Conversely, DeRENs emphasize decentralizing the management and allocation of resources. These networks facilitate the direct peer-to-peer exchange of resources like storage, processing power, and financial assets. By eliminating intermediaries and fostering user autonomy, DeRENs aim to achieve equitable access and scalability, reducing the need for centralized platforms.
Key differences between DePINs and DeRENs will be further elaborated upon in the following sections.
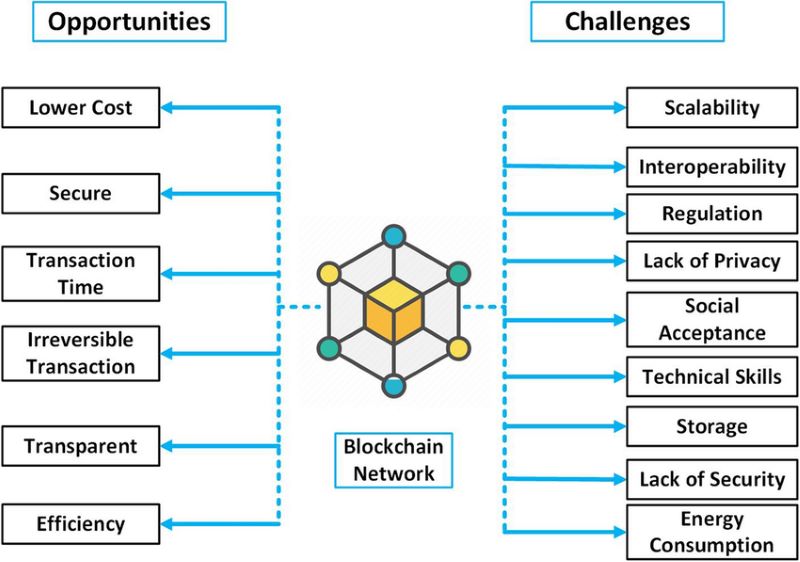
Opportunities and challenges concerning decentralized physical networks
Decentralized physical networks (DePINs) present both opportunities and challenges in transforming infrastructure. On one hand, they offer increased resilience, equitable access to resources, and sustainability through decentralized control. By distributing control and operations, DePINs mitigate single points of failure, making systems more robust against disruptions. They also empower individuals by enabling participation and profit-sharing in shared resources, fostering a more inclusive economy. Furthermore, DePINs promote peer-to-peer transactions and the use of renewable resources, leading to cost-effective and environmentally friendly solutions.
However, significant hurdles remain. Regulatory barriers, scalability limitations, interoperability issues, and infrastructure requirements pose challenges to widespread adoption. Integrating blockchain with physical systems necessitates robust security measures, privacy protections, and user-friendly interfaces. Notably, in heavily regulated sectors like telecommunications, constructive dialogue between industries and DePIN projects is crucial to overcome regulatory obstacles and deliver benefits to users.
In essence, DePINs represent a promising yet complex landscape. Their potential for positive disruption is immense, but success hinges on addressing technical and regulatory challenges while ensuring security and usability.
The future of decentralized physical networks
The future of decentralized physical networks (DePINs) is brimming with potential, leveraging blockchain, IoT, and renewable energy to build resilient, efficient, and community-driven infrastructure across various sectors. From optimizing energy distribution and telecommunications to revolutionizing healthcare and education, DePINs promise to transform how we access and manage essential resources.
However, this promising future requires collaboration among stakeholders, regulatory frameworks that support innovation, and continued technological advancements to overcome challenges and fully realize the potential of decentralized infrastructure. Innovation within distributed networks is key to ensuring the sustainable scalability of these applications.
By establishing the right framework, DePINs can empower individuals and communities to shape a future where infrastructure is decentralized, equitable, and environmentally friendly. This transformative potential has the power to redefine our relationship with essential services and create a more sustainable and interconnected world.
Visit Solution of Blockchain to learn more and unlock the power of decentralized networks.