What is decentralization on demand? What is the difference between decentralization and centralization?
Can’t decide between centralized control and the freedom of decentralization? Discover “decentralization on demand,” a flexible approach that lets you tailor the level of decentralization to your specific needs.
What is decentralization on demand?
In the context of blockchain, “decentralization on demand” is a nuanced concept that goes beyond the standard definition of decentralization. It refers to the ability to adjust the level of decentralization within a system based on specific needs or requirements. This approach acknowledges that complete decentralization may not always be necessary or optimal for every situation.
Instead, decentralization on demand allows for a flexible approach where different aspects of a system or process can be decentralized to varying degrees, depending on factors like security needs, efficiency requirements, and governance preferences.
Why decentralization on demand matters
Decentralization is a concept with varying degrees of implementation and its importance lies in its ability to improve the stability and fairness of a system. When designing technology solutions, three main network architectures are often considered: centralized, distributed, and decentralized. While blockchain technology often employs decentralized networks, a blockchain application itself doesn’t fall into a simple binary classification of being decentralized or not.
Decentralization exists on a spectrum, and it’s essential to assess the level of decentralization applied to various aspects of a blockchain application. By decentralizing the management and access to resources within an application, a more equitable and reliable service can be achieved. However, this often involves trade-offs like reduced transaction throughput. The key lies in determining if the benefits of increased stability and service levels outweigh these trade-offs.
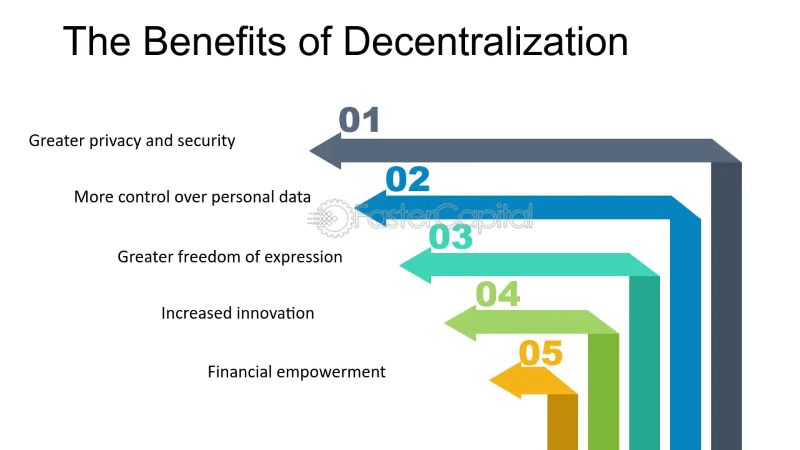
Benefits of decentralization on demand
Decentralization offers numerous benefits, particularly in the realm of blockchain technology.
Firstly, it establishes a trustless environment where participants need not know or trust each other. This is achieved through the distributed ledger, which holds an identical copy of data for each member, ensuring data integrity and preventing unauthorized alterations.
Secondly, decentralization improves data reconciliation between companies. By eliminating the need for data silos and providing a real-time, shared view of the data, it minimizes the risk of data loss or corruption during transfer and transformation.
Thirdly, it reduces vulnerabilities in systems that rely heavily on specific actors. Decentralization distributes control, mitigating the risk of systemic failures due to reliance on a single point of authority.
Finally, decentralization optimizes resource distribution, leading to improved service performance, consistency, and resilience against catastrophic failures. By distributing resources across the network, the system becomes less reliant on any single component, ensuring greater stability and reliability.
Overall, decentralization in blockchain fosters trust, enhances data integrity, minimizes vulnerabilities, and optimizes resource allocation, making it a powerful tool for building robust and equitable systems.
What is the difference between decentralization and centralization?
| Centralized | Distributed | Decentralized | |
| Network/hardware resources
|
Maintained & controlled by single entity in a centralized location | Spread across multiple data centers & geographies; owned by network provider | Resources are owned & shared by network members; difficult to maintain since no one owns it |
| Solution components | Maintained & controlled by central entity | Maintained & controlled by solution provider | Each member has exact same copy of distributed ledger |
| Data | Maintained & controlled by central entity | Typically owned & managed by customer | Only added through group consensus |
| Control | Controlled by central entity | Typically, a shared responsibility between network provider, solution provider & customer | No one owns the data & everyone owns the data |
| Single Point of Failure | Yes | No | No |
| ExFault tolerance | Low | High | Extremely high |
| Security | Maintained & controlled by central entity | Typically, a shared responsibility between network provider, solution provider & customer | Increases as # of network members increase |
| Performance | Maintained & controlled by central entity | Increases as network/hardware resources scale up and out | Decreases as # of network members increase |
| Example | ERP system | Cloud computing | Blockchain |
Who is building blockchain applications leveraging decentralization
Various entities across industries are building blockchain applications that leverage decentralization to varying degrees. This adoption level often depends on the maturity of the solution, the reliability of its incentive models and consensus mechanisms, and the founding team’s ability to strike a balance between decentralization and other factors like efficiency and security.
Many Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) exemplify this diverse approach, with different components exhibiting varying levels of decentralization. For instance, oracles might be partially decentralized, while smart contracts remain centralized, and the governance process for adjusting parameters is community-driven and fully decentralized.
On a broader scale, organizations of all types and sizes are exploring and adopting decentralized blockchain solutions. These applications are found in diverse sectors, ranging from humanitarian aid delivery to personal data management. Notably, blockchain is enabling direct provision of aid in emergencies, bypassing traditional intermediaries. Additionally, it’s empowering individuals to control their digital identities and data, addressing issues of privacy and data exploitation prevalent in the current centralized model.
A real-world example
Contura Energy, a major U.S. coal supplier, traditionally relied on an outdated, manual letters of credit system for international trade payments. While this system offered trust, it was slow and inefficient. Recognizing the need for modernization, Contura is collaborating with AWS to develop a decentralized, blockchain-based solution for managing international trade payments. This innovative approach aims to streamline the process, reduce costs, and minimize risks while enhancing transparency and providing real-time visibility for all parties involved.
Contact Solution of Blockchain today to explore how decentralized technology can transform your operations and unlock new opportunities.