In the blockchain technology industry, DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) and traditional EVM blockchain are two prominent technologies, each offering unique advantages. However, understanding the differences between them is crucial for selecting the right solution for future projects. This article will compare DAG and traditional EVM blockchain, helping you recognize the pros and cons of each technology.
Understanding DAG and EVM technology
Before diving into the differences between DAG and traditional EVM blockchain, it’s important to clarify each of these technologies.
What is traditional EVM Blockchain?
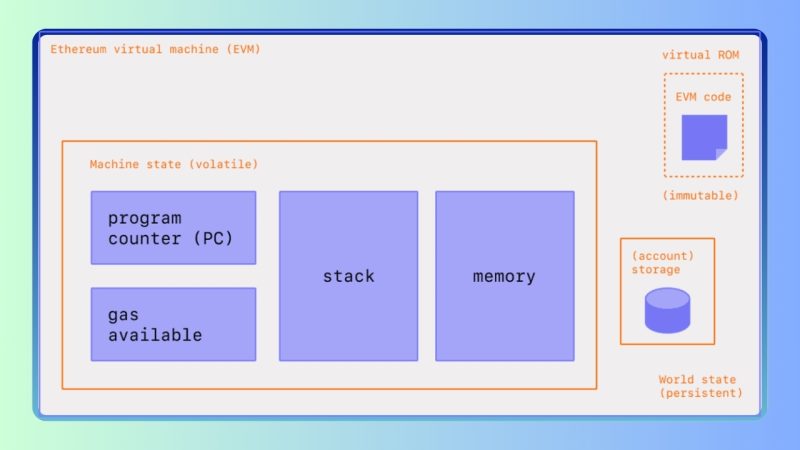
Traditional EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) blockchain is a popular platform for developing smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). This system uses a blockchain structure, where transactions are stored and verified through blocks. These blocks are linked together in a chain, with each block containing data about transactions and a reference to the previous block through a hash function. This creates an immutable and secure data chain.
EVM blockchain operates based on consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), which help verify transactions and ensure system integrity. Notably, Ethereum – the most widely used blockchain platform with EVM – enables developers to build smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
What is DAG technology?
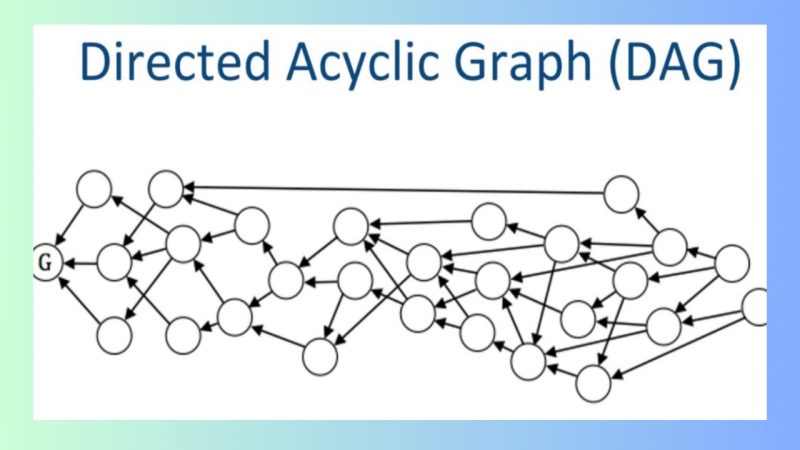
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is a technology that is fundamentally different from traditional blockchain. In DAG, transactions are not stored in a chain but are organized in an acyclic directed graph. Instead of sequential blocks, each transaction in DAG can validate previous transactions, forming a network of parallel and simultaneous transactions.
Features of traditional EVM Blockchain
Blockchain structure
Traditional EVM blockchain operates on a blockchain model where data is stored in consecutive blocks. Each block in the chain contains information about transactions made within a specific timeframe and is linked to the previous block via a hash function. This mechanism ensures data integrity, making each transaction transparent and immutable.
However, this connection creates limitations. Each new block must wait for the previous block to be validated, leading to network congestion when many transactions occur simultaneously. As a result, the processing speed of traditional EVM blockchain is significantly affected during high transaction volumes.
Decentralization and security
One of the greatest strengths of EVM blockchain is decentralization. With thousands of nodes (validation points) distributed globally, it is difficult to cheat or attack the network. Additionally, consensus mechanisms such as PoW or PoS help protect the network from fraudulent activities and ensure transaction security.
However, this also comes with some drawbacks. PoW, in particular, requires a large amount of computational resources, which leads to high energy consumption and increased transaction costs. Although EVM platforms today have transitioned to PoS or other consensus mechanisms to mitigate this issue, transaction costs remain a factor to consider when using traditional EVM blockchain.
Smart contracts and dApps
EVM blockchain is the most popular platform for developing smart contracts, especially on Ethereum. Smart contracts are self-executing programs that automatically enforce the terms of a contract without third-party intervention. This creates an ideal environment for developing decentralized applications (dApps) across various industries, from finance to gaming, art, and many others.
Thanks to the ability to execute smart contracts, dApps on EVM blockchain can operate autonomously without oversight from intermediaries. However, this requires developers to have in-depth programming knowledge and a clear understanding of EVM blockchain’s operating principles.
Features of DAG
Acyclic graph model
DAG is an advanced technology that uses a graph structure instead of a series of blocks like in traditional blockchain. Each transaction in DAG can validate previous transactions, forming a network without cycles. This allows DAG to process thousands of transactions per second without encountering congestion.
However, the absence of blocks in DAG presents some security and decentralization challenges. Without a chain of blocks to validate transactions, DAG networks may be more susceptible to attacks if robust protection mechanisms are not in place. This requires projects using DAG to focus on developing new security systems.
Scalability and transaction processing
One of the greatest advantages of DAG is scalability. Transactions in DAG are not limited by block confirmation speeds, as in EVM blockchain. They can be processed simultaneously and quickly, allowing DAG to handle a large volume of transactions without system congestion.
Moreover, DAG reduces transaction costs. Since there are no large blocks to validate and maintain, DAG requires fewer resources than EVM blockchain, which ultimately reduces transaction costs for users.
Decentralization and security
While DAG has decentralization similar to traditional blockchain, its security can be compromised without strong protective mechanisms since it doesn’t use blocks for transaction validation. The DAG system could be more vulnerable to attacks if transactions are not thoroughly verified.
Projects like IOTA have introduced robust security solutions to address this, but ongoing research and improvements are needed to ensure system safety.
Compare DAG and traditional EVM Blockchain
- Speed and scalability: One of the most apparent differences between DAG and traditional EVM blockchain is scalability and transaction processing speed. DAG excels in processing thousands of transactions per second without encountering congestion. Each transaction can validate previous ones, making the network flexible and unaffected by transaction volume. Meanwhile, traditional EVM blockchain must process each transaction in blocks, leading to delays and higher costs for large-scale transactions.
- Transaction costs: In traditional EVM blockchain, transaction costs can be very high, especially when the network is congested. Gas fees play a crucial role in determining transaction costs, and these fees can fluctuate greatly depending on the Ethereum network’s congestion. On the other hand, DAG helps reduce transaction costs by processing transactions simultaneously without the need for blocks. This makes DAG a viable solution for applications requiring fast and low-cost transactions.
- Security: Traditional EVM blockchain stands out for its high security due to consensus mechanisms like PoW or PoS. The robust decentralization of the network helps protect it from attacks. However, DAG needs to improve its security, as the lack of validating blocks like in traditional blockchain can create security vulnerabilities without appropriate protection mechanisms.
After comparing DAG and traditional EVM blockchain, we can see that each technology has its own strengths and weaknesses. DAG excels in scalability and fast transaction speeds but still requires improvements in security. In contrast, traditional EVM blockchain offers strong security and dApp development capabilities but faces issues with transaction costs and speed during high transaction volumes.
To better understand blockchain technologies and learn more about DAG and traditional EVM blockchain, don’t forget to follow Solution Of Blockchain for detailed and up-to-date articles.