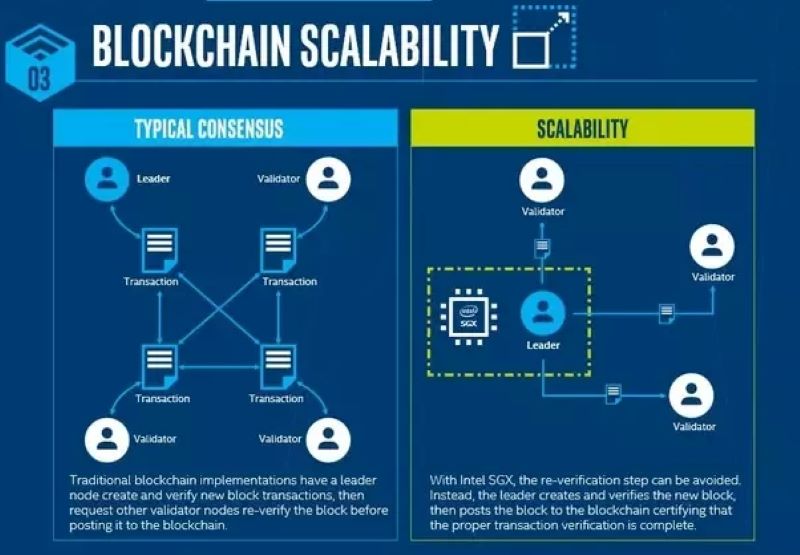
Blockchain scalability: the bottleneck of mass adoption. But fear not! Discover the latest Blockchain Scalability Solutions revolutionizing transaction speed and network capacity, paving the way for a seamless blockchain experience.
Understanding Blockchain Scalability Solutions
Before we explore different scalability solutions, it’s essential to grasp the challenges that blockchain networks face in terms of scalability. These challenges primarily revolve around throughput, the number of transactions processed per unit of time, and latency, the time it takes for a transaction to be confirmed.
Traditional blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum have limited throughput, hindering their applicability in scenarios demanding high transaction volumes. Bitcoin can only handle about 7 transactions per second, while Ethereum’s capacity doesn’t surpass 20. Additionally, high latency in blockchain networks leads to delays in transaction finality, making them unsuitable for applications requiring real-time responsiveness.
In essence, these limitations in throughput and latency pose significant obstacles to the widespread adoption of blockchain technology, especially for use cases like payment systems, supply chain management, online gaming, and high-frequency trading. Understanding these challenges is the first step towards exploring and implementing effective scalability solutions.
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
Layer 2 scaling solutions are designed to address the scalability limitations of blockchains by utilizing the main blockchain as a foundation and processing a substantial portion of transactions off-chain. This strategy significantly enhances the number of transactions the network can process per second, while simultaneously decreasing the time it takes for transactions to be confirmed. As a result, blockchain networks can effectively manage a much greater volume of transactions, improving overall performance and efficiency.
Payment Channels (Off-Chain Transactions)
Payment channels, a key Layer 2 scaling solution, address blockchain scalability by enabling multiple off-chain transactions. Users can conduct numerous transactions within a payment channel, and only the final balance is settled on-chain. This drastically reduces the load on the blockchain, lowering fees and increasing transaction speed.
A prime example of this is the Lightning Network, implemented on Bitcoin and Litecoin. It allows users to open channels, transact off-chain without limitations, and settle the final outcome on the underlying blockchain, demonstrating a practical way to improve blockchain scalability and efficiency.
Learn more Blockchain Knowlegde
Sidechains (Parallel Chains)
Payment channels are a crucial Layer 2 scaling solution designed to address the limitations of blockchain scalability. By enabling multiple transactions to occur off-chain within a dedicated channel, these channels alleviate the burden on the main blockchain. Only the final balance resulting from these off-chain transactions is ultimately settled on-chain. This approach drastically reduces network congestion, resulting in lower transaction fees and significantly faster transaction speeds.
The Lightning Network, implemented on Bitcoin and Litecoin, serves as a prime example of a payment channel solution. It empowers users to establish channels, conduct unlimited transactions off-chain, and ultimately settle the final net balance on the underlying blockchain. This exemplifies a practical and effective method for enhancing blockchain scalability and efficiency, making it more suitable for everyday use.
Sharding
Sharding is a horizontal partitioning method that divides the blockchain into smaller segments called shards. Each shard functions independently, processing its own transactions and smart contracts simultaneously, enhancing the network’s capacity and enabling it to handle a higher volume of transactions. By dividing the blockchain into multiple shards, sharding addresses the scalability bottleneck, resulting in increased throughput and reduced latency.
Ethereum 2.0’s Beacon Chain
Ethereum 2.0, also referred to as ETH2 or Serenity, is a major upgrade designed to enhance Ethereum’s scalability through sharding. A key feature of this upgrade is the introduction of the Beacon Chain, a new chain that serves as the coordinator for the entire Ethereum network. It manages consensus mechanisms and validators, allowing Ethereum to process numerous transactions and smart contracts concurrently, significantly boosting its capacity and overall performance.
Layer 1 Scaling Solutions
Layer 1 scaling solutions directly address the scalability limitations of the core blockchain itself, rather than relying on external layers or off-chain mechanisms. They focus on enhancing the underlying consensus algorithm and data structure to boost the network’s capacity for processing transactions and decreasing the time it takes to confirm them.
Proof of Stake
Proof of Stake (PoS) is an alternative consensus algorithm to Proof of Work (PoW), used in Bitcoin and Ethereum 1.0. Unlike PoW, PoS chooses validators based on their network stake rather than computational power. By eliminating the energy-intensive mining process, PoS significantly enhances the scalability of blockchain networks and reduces their environmental footprint.
Cardano is a notable example of a blockchain utilizing PoS, showcasing its potential for improved scalability and reduced environmental impact compared to PoW-based networks.
Sharding
Sharding is not solely a Layer 2 scaling solution. It can also be integrated directly into the base layer of a blockchain (Layer 1) as part of its consensus protocol. This allows for the efficient distribution of transactions and smart contracts across multiple shards within the network itself.
A prominent example of this is Zilliqa, a blockchain platform that natively employs sharding as its primary method for achieving scalability. This innovative approach enables Zilliqa to process a remarkable number of transactions per second, making it a highly scalable solution suitable for diverse applications, particularly in decentralized finance and gaming.

Blockchain scalability has been a persistent challenge hindering its widespread adoption. However, the industry is making significant strides with innovative solutions like layer 2 scaling, sharding, and layer 1 improvements like proof of stake. These advancements are paving the way for a more scalable future for blockchain technology, addressing concerns about transaction speed, cost, and efficiency.
As these solutions continue to evolve and mature, we can anticipate a broader range of blockchain applications, from high-volume payment systems to real-time gaming platforms. The ability to handle a vast number of transactions per second with minimal latency will unlock new opportunities and propel blockchain integration into our daily lives.
The future of blockchain scalability is promising, with ongoing research, development, and collaboration within the blockchain community driving the evolution of this transformative technology. As these efforts continue, we can expect a more decentralized, efficient, and scalable blockchain ecosystem that can meet the demands of a growing number of users and applications.
Don’t let scalability limitations hold you back – embrace the future of blockchain with Solution of Blockchain.