Bitcoin blockchain technology – the revolutionary technology behind the world’s first cryptocurrency. Discover how this decentralized ledger is transforming finance, ensuring secure and transparent transactions without intermediaries.
What is the Bitcoin blockchain technology?
The Bitcoin blockchain, created in 2008, is a groundbreaking decentralized technology that underpins the Bitcoin cryptocurrency and many others. It revolutionizes how we perceive money and transactions by offering a transparent, secure, and tamper-proof system.
At its core, the Bitcoin blockchain is a digital ledger that records transactions in blocks, which are then linked together in a chronological chain. Each block contains a collection of Bitcoin transactions from a specific period, and this chain of blocks ensures the immutability of the data. Once a block is added, it cannot be modified, providing a secure and verifiable record of every transaction.
A unique aspect of the Bitcoin blockchain is its decentralized nature. It is not stored on a single computer or controlled by a single entity, but rather distributed across a network of computers, making it resilient to attacks and failures.
The blockchain uses cryptographic hashes, unique codes for each block, to maintain the integrity of the chain. Each block’s hash incorporates the hash of the previous block, creating a chain of linked blocks where any tampering with a single block would invalidate the entire chain.
The Bitcoin blockchain consists of two types of records: block records, containing the latest Bitcoin transactions, and transaction records, which detail the assets, prices, and ownership data. These records are validated and settled across all nodes in the network within seconds, ensuring transparency and accuracy.
The Bitcoin blockchain has significantly impacted the financial world, offering an alternative to traditional banking systems and paving the way for a more decentralized and secure financial future.
Short story of Bitcoin blockchain technology
The concept of blockchain technology dates back to 1991, but it wasn’t until the creation of Bitcoin in 2008 that its full potential was realized. Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, was designed to revolutionize the financial world by enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries like banks.
However, innovators quickly recognized that blockchain technology had broader applications beyond cryptocurrency. The Bitcoin blockchain was engineered to store a variety of data, not just information related to Bitcoin transactions.
This decentralized peer-to-peer network consists of thousands of Bitcoin nodes, each holding a copy of the blockchain and contributing to its maintenance and security. It operates without a central authority, relying on the collective effort of its participants to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the ledger.
Peer-to-peer transactions are at the heart of Bitcoin’s functionality. These transactions involve the exchange of information between users’ wallets, including location and IP address data, enabling direct interactions without intermediaries. This decentralized approach to financial transactions represents a significant departure from traditional banking systems, offering greater autonomy and security to users.
What is needed to make the Bitcoin blockchain work technology ?
The Bitcoin blockchain, as a decentralized system for trustless transactions, eliminates the need for intermediaries like banks to maintain financial records. Instead, every participant in the network possesses a copy of the ledger, ensuring transparency and security.
This blockchain network is where Bitcoin transactions occur, involving mining and the generation of hash power, which is the computational power required to solve complex algorithms for creating and trading cryptocurrencies.
Bitcoin owners typically acquire their cryptocurrency through exchanges, platforms that facilitate Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency transactions. The decentralized ledger is the foundation of the blockchain network, recording every action within the system.
Each block in the blockchain contains multiple transactions, and every new transaction is added to the ledger of each participant, creating a transparent and immutable record. This distributed database is managed by multiple participants using distributed ledger technology (DLT).
Blockchain, a type of DLT, secures transactions with immutable cryptographic signatures called hashes. Each block includes the hash of the previous block, forming a chain of linked blocks, hence the term “blockchain.” This chaining mechanism ensures data integrity and prevents tampering, making blockchain a secure and reliable technology for various applications.
The Bitcoin blockchain functions as a self-verifying ledger that records every transaction. A vast network of nodes, or computers participating in the network, continuously checks and secures each transaction. Miners play a crucial role in this process, utilizing their computational power to maintain the blockchain and receive Bitcoin as a reward. This entire set of rules governing the network is known as the Bitcoin protocol.
Bitcoin miners are essentially high-powered computers that solve intricate mathematical problems to create new bitcoins, a process known as mining. These dedicated machines verify all transactions, ensuring their legitimacy and preventing fraudulent activity. Miners gather multiple transactions into a block, verify its accuracy, and add it to the existing chain of blocks using a mathematical method. In return for their computational contributions, miners are rewarded with newly minted Bitcoin.
How does the Bitcoin blockchain technology work?
While both blockchain and databases are methods for storing information electronically, they differ significantly in structure and function.
Databases typically organize data in tables, facilitating easy search and filtering for multiple simultaneous users. They rely on powerful servers to store and manage vast amounts of data, allowing for quick access and editing.
Blockchain, on the other hand, structures data into blocks with a specific storage capacity. Once a block is filled, it’s chained onto the previous block, forming an unchangeable timeline. This chain-like structure makes blockchain a more complex type of database, especially in decentralized systems.
The key difference is that blockchain is designed to be immutable, meaning the data recorded in blocks cannot be altered once added to the chain. This ensures the integrity of the data over time, with each block time-stamped for transparency.
The purpose of blockchain is to enable the recording and distribution of digital information without allowing any edits. This immutability sets it apart from traditional databases, where data can be modified.
The emergence of Bitcoin marked the first practical application of blockchain technology. By using blockchain to create a decentralized ledger for recording Bitcoin transactions, it demonstrated the potential for secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record-keeping, paving the way for a multitude of applications beyond cryptocurrency.
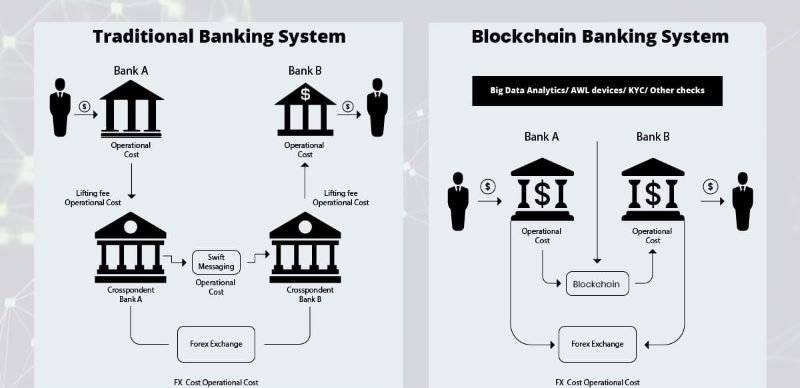
Blockchain vs. banks
The Bitcoin blockchain operates fundamentally differently from traditional banks, primarily due to its decentralized nature. It relies on a network of thousands of computers to validate transactions, ensuring continuous operation 24/7, unlike banks with fixed operating hours.
One of the most significant advantages of the Bitcoin blockchain is its transparency. It acts as a public ledger, recording every transaction within the network, fostering trust and accountability. This contrasts sharply with traditional banking, where transaction records are often private and inaccessible to the public.
However, transaction speeds on the Bitcoin blockchain can vary, ranging from 15 minutes to over an hour, depending on network congestion. This is slower than card payments or check deposits, which typically take 24 to 72 hours to clear.
Additionally, Bitcoin transaction fees fluctuate, typically ranging from $0 to $50. Unlike banks, where fees may be based on the transaction amount, Bitcoin fees are influenced by network conditions and transaction size, as each block has a limited data capacity.
Furthermore, the Bitcoin blockchain allows anyone with an internet connection to participate in transactions, while traditional banking often requires an account and specific devices like mobile phones or computers.
These differences highlight the disruptive potential of blockchain technology. Its decentralized nature, tamper-proof records, and transparency make it a compelling alternative to traditional financial systems, offering users greater control and security over their assets.
Explore our comprehensive resources and expert insights at Solution of Blockchain to stay ahead of the curve.