A Beginner Guide to Understanding Blockchain
Beginner guide to understanding blockchain: Learn the basics of decentralized networks, secure transactions, and more. Start understanding blockchain today!
Introducing Blockchain
Blockchain, pioneered by Satoshi Nakamoto, revolutionizes data distribution through decentralization. Its core attributes, including durability, transparency, and robustness, redefine data management. Initially designed for Bitcoin transactions, blockchain’s potential extends to various business realms like crowdfunding, smart contracts, and supply chain auditing. This introduction sets the stage to explore blockchain’s transformative impact on diverse industries and its potential applications beyond cryptocurrency transactions.
Benefits and features of blockchain technology
Decentralization: Being decentralized means that no single entity controls the blockchain network. Instead, it is maintained by a network of computers, enhancing security and resilience against tampering or fraud.
Immutability: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes extremely difficult to alter or delete. This immutability ensures the integrity of the data and enhances trust among users.
Transparency: All transactions and data stored on the blockchain are visible to all participants, promoting transparency and accountability. This transparency fosters trust and allows for easier tracking and verification of transactions.
Security: Blockchain employs cryptographic techniques to secure data and validate transactions, making it highly resistant to cyber-attacks and fraud. This ensures the integrity and confidentiality of the data stored on the blockchain.
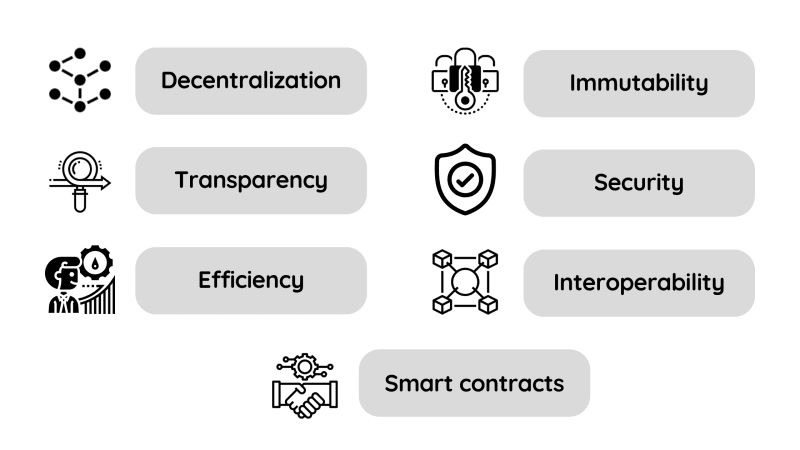
Efficiency: By automating processes and eliminating intermediaries, blockchain technology can streamline transactions, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. This efficiency improvement benefits various industries by speeding up processes and reducing overheads.
Interoperability: Blockchain facilitates the exchange of data and assets between different systems and platforms, enhancing interoperability and reducing complexity in processes. This interoperability enables seamless integration with existing systems and promotes collaboration across industries.
Smart contracts: Blockchain enables the creation and execution of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with predefined terms written in code. Smart contracts automate processes and enforce agreements, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing efficiency in specific operations.
Process of adding new blocks to the chain
What does consensus do in blockchain?
Consensus algorithms regulate how nodes within the blockchain network agree on the state of the ledger. They establish rules for ensuring consensus among nodes regarding the validity of transactions and the current state of the blockchain. Various consensus algorithms exist, including proof of work, proof of stake, and delegated proof of stake, each with its own approach to achieving agreement and maintaining network integrity.
Different types of the blockchain
| Public blockchains | Private blockchains | Consortium blockchains |
|---|---|---|
| Public blockchains are open to anyone and are secured through the mining process. | Private blockchains are restricted to a specific group of users and are not secured through mining. | Consortium blockchains are a hybrid of public and private blockchains. |
| Examples of public blockchains include Bitcoin and Ethereum. | Used in industries such as finance and healthcare, where the need for security and privacy is high. | Hyperledger is an example of a consortium blockchain. |
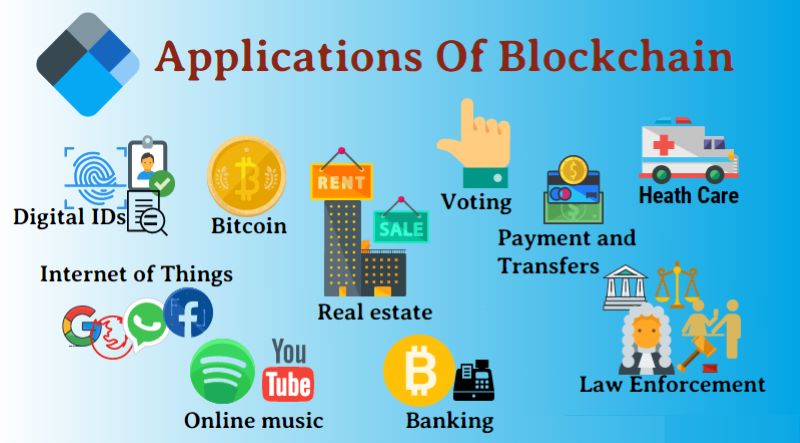
Applications of blockchain
Blockchain technology has vast potential across a spectrum of industries, offering innovative solutions to various challenges. Here are several applications showcasing its versatility:
Cryptocurrencies: Blockchain’s pioneering application, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, leverage its decentralized ledger for secure, transparent transactions.
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain enhances supply chain transparency and efficiency by tracking product movement, ensuring authenticity, and reducing fraud.
Identity Verification: Blockchain enables secure, immutable digital identities, streamlining identity verification processes for individuals and organizations.
Smart Contracts: Blockchain facilitates the creation of self-executing contracts, automating transactions and enforcing terms when predefined conditions are met.
Voting Systems: Blockchain-based voting systems ensure secure, transparent elections, mitigating fraud and enhancing trust in democratic processes.
Health Records: Blockchain secures electronic health records, improving data accuracy, accessibility, and privacy in healthcare systems.
Real Estate: Blockchain streamlines property ownership and transfer processes, providing immutable records and reducing administrative burdens in real estate transactions.
Education: Blockchain verifies and tracks educational credentials, simplifying credential verification for employers and institutions.

The future of blockchain
Increased Adoption: With growing awareness of blockchain’s benefits, adoption across industries and organizations is expected to rise, driving its integration into mainstream business processes.
New Consensus Algorithms: Continuous research and development will lead to the emergence of new consensus algorithms, enhancing security, efficiency, and scalability of blockchain networks.
Improved Scalability: Addressing scalability challenges remains a priority, prompting the exploration of innovative solutions to boost transaction throughput and network performance.
Integration with Emerging Technologies: Blockchain’s synergy with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and IoT will foster the creation of novel solutions, unlocking new possibilities and use cases.
Heightened Regulation: As blockchain becomes more pervasive, regulatory frameworks will evolve to ensure compliance, foster trust, and protect users, fostering a conducive environment for its sustainable growth.
Expansion of Decentralized Applications (dApps): The proliferation of decentralized applications will continue, offering decentralized, secure, and transparent alternatives across various domains, driving user adoption and ecosystem growth.
Dive into the world of blockchain with our beginner’s guide! From decentralized networks to secure transactions, we’ve covered it all to help you grasp the fundamentals. Start your journey to understanding blockchain today and unlock the potential of this transformative technology!
Follow Solutions of Blockchain for more information