Both Blockchain technology and Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) are crucial platforms in the modern blockchain ecosystem, yet each technology has its unique features and applications. In this article, we will analyze the differences between the technology of DAG compared to traditional Blockchain, giving you a clearer view of the advantages and disadvantages of each technology.
Traditional Blockchain technology
Traditional Blockchain is a technology for storing and verifying transactions based on a chain of blocks linked together in chronological order. Each block in the chain contains transactions and a hash of the previous block, forming a continuous chain that ensures data integrity. Traditional Blockchain operates on a decentralized principle, meaning copies of the blockchain are stored and synchronized across many nodes in the network, ensuring security and immutability of the information.
DAG technology
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a distributed data structure used in various blockchain applications, especially in systems that require high scalability and fast transaction speeds. Unlike traditional Blockchain, DAG uses a directed graph with no cycles to link transactions. In a DAG system, each transaction is confirmed by directly connecting to other transactions, rather than being grouped into blocks as in traditional Blockchain.
The technology of DAG compared to traditional Blockchain
Both traditional Blockchain and Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) are distributed platforms used in many blockchain applications. However, they differ significantly in terms of operation, advantages, disadvantages, and real-world applications. Below is a detailed comparison of DAG technology compared to traditional Blockchain.
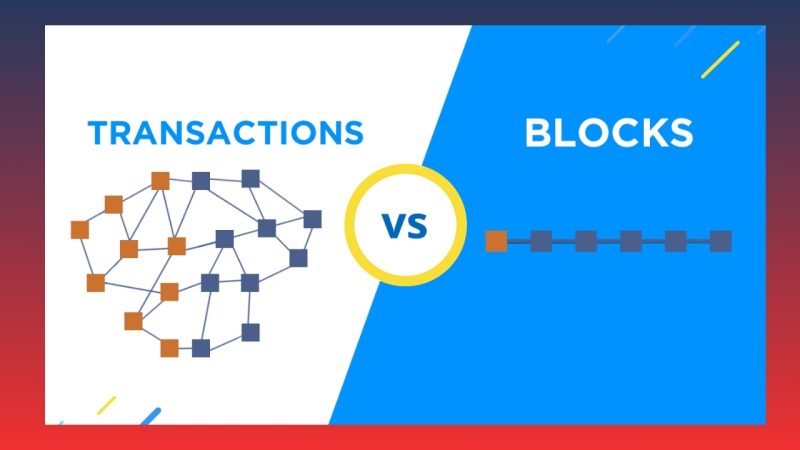
Structure and operating principles
Traditional Blockchain
- Structure: Blockchain consists of a chain of blocks containing transactions, connected in a continuous sequence. Each block contains a group of transactions and a hash of the previous block, forming a chain.
- Operating principle: Each new block can only be added to the chain after the previous block has been validated and recorded, ensuring data integrity. Transactions within each block are processed sequentially, and only after all transactions in a block are confirmed can the next block be created.
DAG technology
- Structure: Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a directed, acyclic graph. Instead of grouping transactions into blocks, in DAG, each transaction is directly linked to previous and subsequent transactions, forming a cycle-free, interconnected network.
- Operating principle: In DAG, transactions do not need to wait for a new block to be confirmed; they are processed concurrently and in parallel. Transactions are confirmed immediately when they connect with other transactions, creating a decentralized network without the need for blocks.
Scalability
Traditional Blockchain
Traditional Blockchain has scalability limitations, especially in systems using consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). Each block can only contain a fixed number of transactions and must be processed sequentially. This leads to network congestion and reduces transaction speed as the number of users and transactions increases.
DAG technology
DAG offers significantly better scalability compared to traditional Blockchain. Since transactions in DAG can be processed simultaneously without relying on adding new blocks to the chain, DAG can handle large volumes of transactions at much faster speeds. The DAG network can scale without experiencing the congestion issues found in traditional Blockchain.
Transaction costs
Traditional Blockchain
Transaction costs in traditional Blockchain can be quite high, especially for networks using the Proof of Work (PoW) mechanism. Mining blocks requires significant computational resources, leading to high transaction costs. Additionally, with network congestion, transaction costs can spike when transaction demand is high.
DAG technology
Transaction costs in DAG-based networks are much lower than those in traditional Blockchain. Since DAG does not rely on mining, there are no miners involved, which significantly reduces transaction costs. This is particularly important for applications requiring fast transaction speeds and low costs, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and online payment services.
Transaction speed
Traditional Blockchain
Transaction speed in traditional Blockchain can be limited by the consensus mechanism and congestion when there are many transactions. For example, the Bitcoin network can handle only about 7 transactions per second (TPS), while Ethereum can process around 30 transactions per second. Transaction confirmation time can vary from a few minutes to several hours depending on network conditions.
DAG technology
Transaction speed in DAG is extremely fast, as transactions do not have to wait for a new block to be confirmed. In DAG systems, transactions can be processed almost immediately, helping to increase transaction speed and significantly reduce latency compared to traditional Blockchain.
Security
Traditional Blockchain
Security in traditional Blockchain is ensured through strong consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake. Major networks such as Bitcoin and Ethereum have demonstrated high levels of security over many years of operation. These algorithms prevent attacks and ensure data integrity.
DAG technology
Security in DAG has not been proven over time like traditional Blockchain. While DAG can process transactions more quickly and efficiently, its security has not been tested and proven through large-scale attacks. The lack of a standard consensus mechanism, as seen in traditional Blockchain, may create potential vulnerabilities in security.
Real-world applications
Traditional Blockchain
Traditional Blockchain is widely used in finance, particularly in cryptocurrency networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum. It is also applied in smart contracts, supply chains, and data security.
DAG technology
DAG is being applied in systems that require high transaction speed and low costs, such as IOTA, a prominent project using DAG in its network to provide fee-free transactions with fast speeds. DAG also has potential applications in IoT, micro-payments, and cloud services.
Both DAG technology and traditional Blockchain have their respective advantages and disadvantages. Traditional Blockchain has proven security and stability over time but struggles with scalability and low-cost transaction processing. On the other hand, DAG offers superior scalability and lower transaction costs, but its security and consensus mechanisms have not been tested in large-scale environments.
The choice of the appropriate technology depends on the requirements of each project. If speed and scalability are priorities, DAG may be the ideal choice. However, if a strong and time-tested security system is needed, traditional Blockchain remains the best option.
Solution Of Blockchain hopes this article has helped you gain a better understanding of the two prominent technologies today and the differences between the technology of DAG compared to traditional Blockchain. If you have any questions about this article, feel free to leave a comment below, and we will support you as soon as possible!