In the world of cryptocurrency, Blockchain has become a technological icon. However, Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is emerging as a superior potential solution, overcoming inherent limitations in speed, cost, and scalability. So, what is DAG Blockchain? Let’s explore the differences and potential of this technology in the article below.
What is DAG Blockchain?
Basic definition of DAG Blockchain
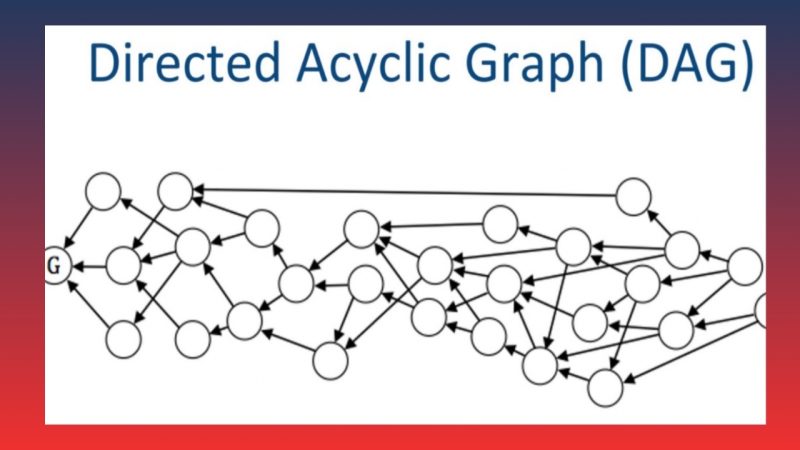
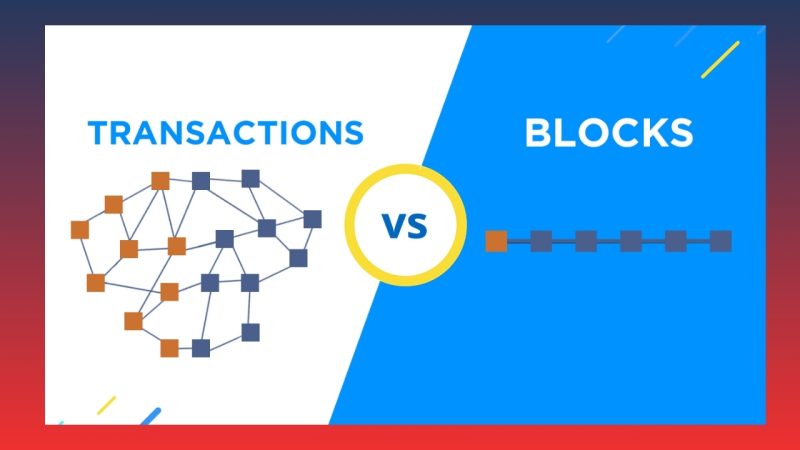
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a directed graph structure that does not contain any cycles. This revolutionary design optimizes transaction storage and processing. In DAG Blockchain, each transaction is organized as a node within the network, and each node references at least two previous transactions. This creates a coherent linked structure, eliminating the need to group transactions into blocks as in traditional Blockchain.
The core of DAG lies in its ability to process decentralized transactions without the need for miners or complex consensus algorithms. Instead of waiting for transactions to be grouped into blocks and validated, each transaction in DAG is validated almost instantly once added to the network. This significantly speeds up processing and reduces transaction costs.
The graph structure of DAG
Some key characteristics of DAG include:
- Directed graph: Transactions are arranged in chronological order, forming a clearly defined directed network.
- No cycles: There are no loops within the structure, ensuring that data cannot be reverted to a previous state.
With this design, DAG allows for simultaneous processing of thousands of transactions, optimizing performance. Additionally, the elimination of the “block” concept in DAG helps mitigate issues like the block size limits seen in traditional Blockchain.
Blockchain vs. DAG
Blockchain: The core technology for traditional cryptocurrencies
Blockchain is the foundational technology that powers well-known cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many other decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. It operates on the principle of linking blocks, where each block contains recorded transactions and must be validated by the network through consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
Key benefits of Blockchain
- High security: Blockchain provides a high level of security due to its strong consensus mechanism. Each block is linked to the previous block, ensuring data integrity and preventing attacks.
- Decentralization: Blockchain does not rely on a single entity, enhancing transparency and independence, thereby maintaining system integrity.
- Smart contract support: Blockchain platforms like Ethereum support the development of smart contracts, enabling the deployment of complex financial and non-financial applications.
Drawbacks of Blockchain
- Slow processing speed: With an increasing number of transactions, Blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum face congestion issues. Each transaction must be validated through consensus, resulting in long waiting times.
- High costs: Transaction fees on Blockchain networks can be very high, especially during peak transaction times, which can be burdensome for users.
- Environmental concerns: Systems based on PoW, like Bitcoin, require large amounts of energy for mining, having a negative environmental impact.
DAG: A modern and efficient solution
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a graph structure without cycles, where transactions are linked directly rather than grouped into blocks. DAG Blockchain optimizes transaction speed and efficiency in a decentralized network without requiring mining.
Key differences between Blockchain and DAG
- Concurrent transaction processing: DAG does not need to group transactions into blocks for processing. Each transaction in DAG can validate and link directly to the previous transaction, speeding up processing and reducing wait times.
- Low costs: Since DAG does not require mining, it doesn’t need specialized hardware and consumes far less energy than Blockchain. This significantly reduces operational costs, with transaction fees often close to zero.
- Superior scalability: DAG can handle millions of transactions per second, unhindered by block size limits. This gives DAG robust scalability, especially in high-speed transaction environments like the Internet of Things (IoT) and microtransactions.
However, DAG Blockchain still faces several challenges:
- Decentralization: Some DAG networks have not yet achieved the level of decentralization seen in Blockchain. DAG projects need to improve consensus mechanisms and security to avoid issues like spam attacks or lack of transparency.
- Incomplete security: Although DAG offers advantages in speed and cost, its security isn’t as robust as Blockchain. Low transaction fees can make the network vulnerable to attacks if not protected by strong security measures.
Thus, both Blockchain and DAG Blockchain have their strengths and weaknesses, and choosing between the two technologies depends on specific needs and applications:
- Blockchain remains the best choice for applications requiring high security and transparency, such as cryptocurrencies and smart contracts. However, issues like speed and cost can limit Blockchain’s scalability in certain cases.
- DAG Blockchain is ideal for applications that require high transaction speed, low cost, and good scalability, such as microtransactions or IoT applications. However, further improvements in decentralization and security are needed for DAG to become a comprehensive solution.
Although Blockchain and DAG Blockchain share many common goals in the development of decentralized ecosystems, their operational differences make each technology suitable for different applications.
Practical applications of DAG Blockchain
IOTA and Tangle: DAG for IoT
IOTA is one of the pioneering projects using DAG through its Tangle model. With the goal of creating a fee-free and fast transaction platform for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, IOTA’s Tangle demonstrates the advantages of DAG.
Benefits
- No transaction fees.
- Processes thousands of transactions per second, supporting communication between IoT devices.
U2U Network: DAG combined with interledger protocol (ILP)
U2U Network utilizes DAG to achieve high transaction performance while integrating the Interledger Protocol (ILP) to enable interoperability between different Blockchain systems.
Applications
- Supports smart contracts compatible with EVM.
- Connects traditional financial systems with Blockchain networks.
Nano and Block-Lattice: DAG solution for fast payments
Nano uses a unique DAG structure called Block-Lattice, where each account has its own Blockchain. This design makes Nano transactions nearly instantaneous and fee-free, ideal for small-value transactions.
The future and potential of DAG Blockchain
Future trends of DAG technology
DAG Blockchain is gaining attention from developers and businesses due to its superior speed and transaction cost efficiency. However, for widespread adoption, this technology still needs improvements and further optimization.
- Enhancing security: One of the biggest challenges for DAG is network security. In DAG, transaction validation primarily relies on nodes referencing each other, making it susceptible to spam attacks. To address this, many projects are developing anti-spam mechanisms, such as light Proof of Work (PoW) algorithms or new consensus mechanisms to enhance security.
- Supporting smart contracts: Currently, DAG is mainly used for digital asset transactions or IoT communication. However, to expand its use, DAG needs to support smart contracts similar to Ethereum. Integrating this feature would open up opportunities for DAG applications in decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and NFTs.
- Cross-Chain interoperability: As the Blockchain industry diversifies, interoperability between different ecosystems becomes crucial. DAG is being researched to integrate the Interledger Protocol (ILP), allowing DAG networks to communicate with traditional Blockchains like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, or Solana.
DAG as a potential replacement for traditional Blockchain
DAG Blockchain is not just a potential alternative; it could become the next step in decentralized technology. The advantages of DAG in speed, cost, and scalability make it suitable for high-performance applications.
- Superior transaction speed: DAG enables the processing of thousands of transactions per second (TPS), far surpassing traditional Blockchains. This is especially suited for applications requiring high speed, such as microtransactions or communication within IoT networks.
- Low cost and Eco-friendly: Unlike Blockchain networks based on PoW, DAG does not require complex mining, saving energy and reducing operational costs. This makes DAG an ideal solution amidst growing concerns about the environmental impact of cryptocurrencies.
Potential application fields for DAG
- Internet of Things (IoT): With its lightweight structure and ability to process transactions in parallel, DAG is well-suited to manage communications between IoT devices. For example, devices can automatically pay service fees or share data securely and quickly.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DAG can serve as a platform for DeFi protocols due to its fast processing and low transaction costs. Additionally, DAG networks can integrate with existing DeFi Blockchains to provide more efficient financial services.
- Supply chain management: In supply chains, speed and transaction transparency are critical. DAG can track and verify each step of the supply chain, ensuring data integrity and reducing operational costs.
Challenges to overcome
Despite its many advantages, DAG still faces some limitations:
- Decentralization: Many existing DAG networks have not yet achieved the level of decentralization that traditional Blockchain networks have. Developers need to ensure that all transactions and data are protected by strong decentralized mechanisms.
- Maturity of the ecosystem: Compared to Blockchain, the DAG ecosystem is still in its infancy. This requires more investment in developing practical applications, user communities, and technical standards.
Long-Term potential of DAG
In the future, DAG could become a cornerstone technology in fields requiring high speed and low cost. With continuous development, DAG may not only replace Blockchain but also open up new opportunities for applying decentralized technology in everyday life.
- Scalability: DAG promises to process global transactions without the limitations of speed or cost.
- Applications in the digital economy: With the rise of the digital economy, DAG could become the foundation for payment ecosystems, e-commerce, and digital services.
DAG Blockchain offers a promising new direction for the cryptocurrency and decentralized technology industries. With its outstanding advantages in speed, cost, and scalability, DAG is gradually asserting its role in IoT, finance, and global transactions. However, to truly replace Blockchain, this technology needs further development to ensure security and decentralization.
We hope this article has helped you better understand “What is DAG Blockchain?” Don’t forget to follow Solution Of Blockchain for more useful insights on the investment and finance market!